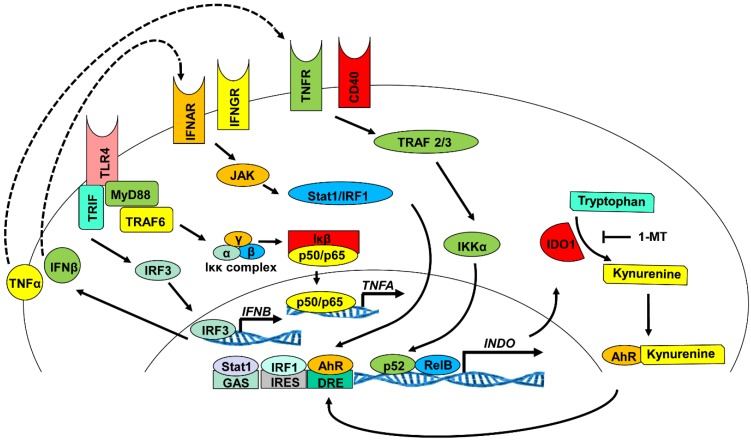
Figure 2.
Mechanism of IDO1 induction in dendritic cells: transcription and translation. Several molecular stimuli and signaling pathways were shown to induce the transcription and translation of metabolically-active IDO1 enzyme [35,40,50]. The IDO1 promoter contains nucleotide sequences that allow regulation of transcription through interferon sequence response-like element (ISRE) upstream consensus sequences, GAS (palindromic gamma-activated sequences) and non-canonical nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cells (NF-κB) [42,50]. In addition, the IDO1 promoter region contains three partial non-canonical RelB/p52 binding sites: AGGAGACACA, GGGAGACAGA and AGGAGAAAGA located near position −2000, which is located downstream of NF-κB-driven IDO upregulation following stimulation of the TLR4, INFGR, IFNAR, TNFR and CD40R signaling pathways [43].