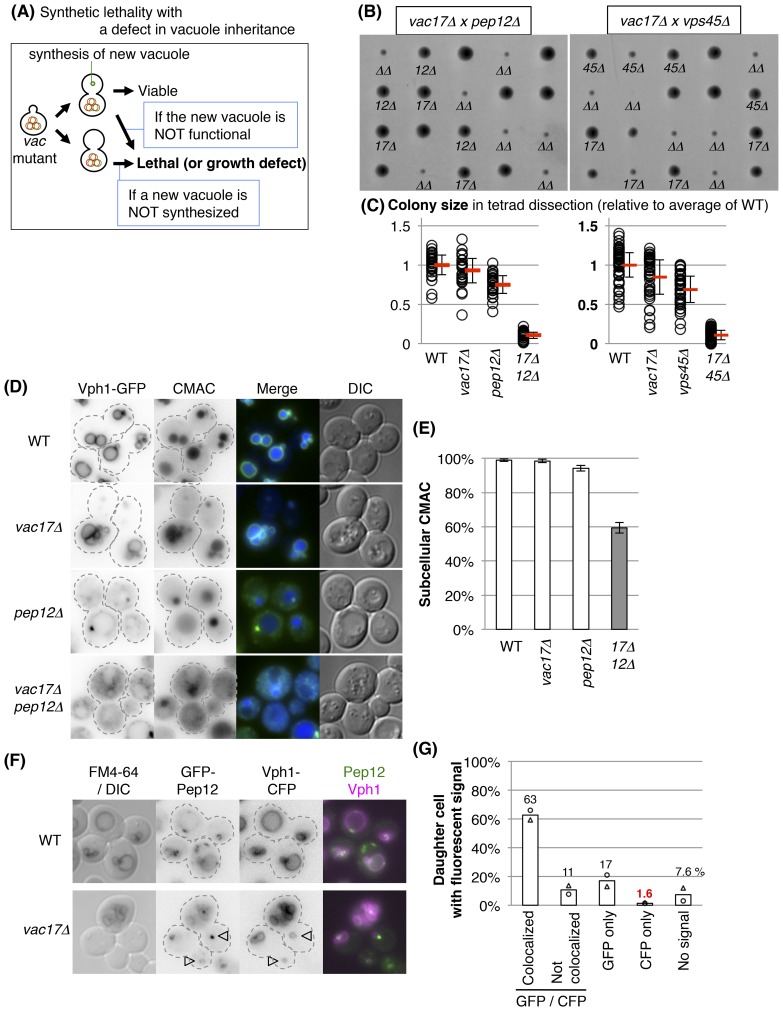
Figure 2. Pep12 and Vps45 are required for the synthesis of a new vacuole.
(A) Schematic of pathways predicted to exhibit synthetic lethality with mutations in vacuole inheritance. When vacuole inheritance is defective, the bud generates a new vacuole that is independent of the mother vacuole. If vacuoles play an essential role, then cells with no mechanism to generate a vacuole will not be viable. Furthermore if the new vacuole is defective in its essential function(s), the cell will not be viable. (B) The pep12Δ and vps45Δ mutants exhibit a synthetic growth defect with vac17Δ. Results of tetrad dissection. Haploid colonies from tetrads derived from heterozygous diploids of VAC17/vac17Δ PEP12/pep12Δ and VAC17/vac17Δ VPS45/vps45Δ were arrayed vertically on YPD (rich medium) plates incubated at 24°C for 3 days. vac17Δ = 17Δ; pep12Δ = 12Δ; vps45Δ = 45Δ; vac17Δ pep12Δ or vac17Δ vps45Δ double mutant = ΔΔ are indicated. (C) Quantification of colony size, relative to the average of wild-type colonies. A total of 28 full tetrads and 48 full tetrads were analyzed for vac17Δ pep12Δ and vac17Δ vps45Δ, respectively. Average size in each genotype (red bar). Error bar; SD. (D) Both vacuole inheritance and new synthesis are important to maintain functional vacuoles. In the vac17Δ pep12Δ mutant several cells appear to lack a vacuole. Wild-type cells incubated with 10 μM CMAC for 30 min exhibited a blue fluorescent signal in the vacuole lumen. The limiting membrane of the vacuole is indicated by Vph1-GFP expressed from its endogenous locus. Wild-type and vac17Δ cells show normal localization of Vph1-GFP and CMAC. Single pep12Δ cells show abnormal distribution in Vph1-GFP, but not CMAC. The vac17Δ pep12Δ double mutant cells show defects in the localization of Vph1-GFP and CMAC. (E) Quantification of cells with a CMAC positive subcellular structure. Any CMAC containing structure with or without Vph1-GFP was scored as a structure. Error bars; SD calculated from four independent experiments with at least 100 cells counted in each strain/experiment. (F) New vacuoles are generated from Pep12-positive endosomes. GFP-Pep12/Vph1-CFP expressed in wild-type and vac17Δcells were pulse labeled with FM4-64. GFP-Pep12 and Vph1-CFP were expressed from the endogenous loci in both strains. Open arrowheads; new vacuoles. (G) Quantification of percent daughter cells with Vph1-CFP and/or GFP-Pep12 in vac17Δ cells. Averages from two independent experiments; at least 100 cells counted per experiment. Open circles and triangles indicate each experiment.