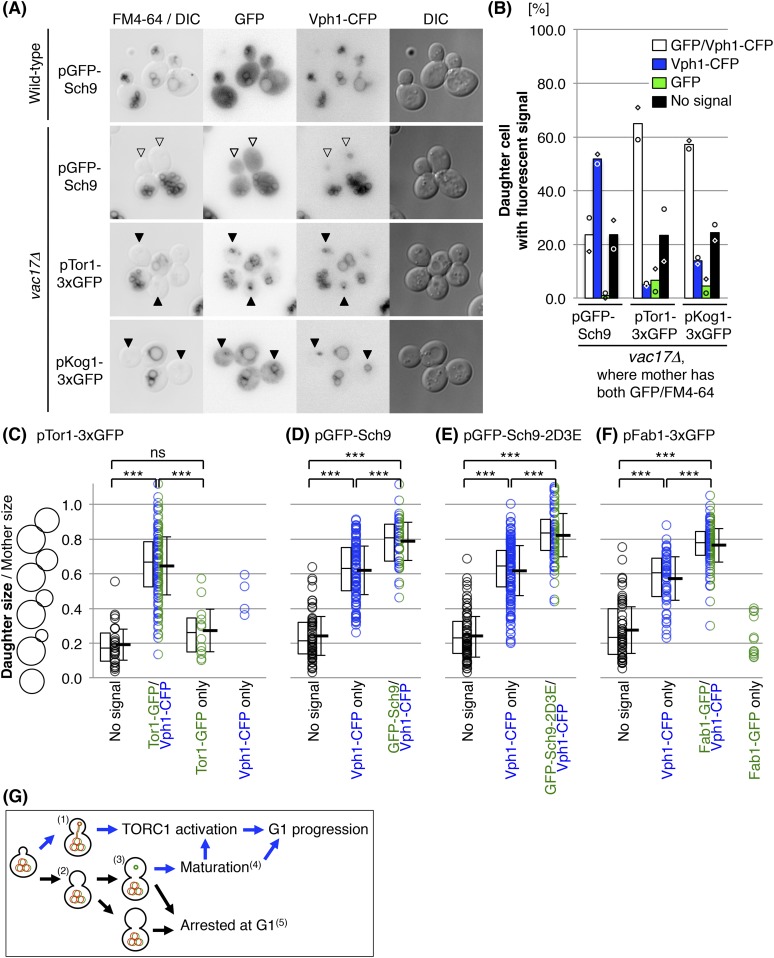
Figure 5. The newly synthesized vacuoles initially lack Sch9 and Fab1.
(A) Sch9 does not localize to the newly formed vacuole. Indicated plasmids were transformed into wild-type and vac17Δ strains, which express Vph1-CFP from its endogenous locus: pRS416 GFP-SCH9, pRS416 TOR1-3xGFP(D330), or pRS416 KOG1-3xGFP. Transformed cells were pulse labeled with FM4-64. Open arrowheads indicate a newly formed vacuole (Vph1-CFP) that was not inherited (lack of FM4-64), and is lacking GFP-Sch9. Closed arrowheads indicate a newly formed vacuole (Vph1-CFP) that was not inherited (lack of FM4-64), and with the GFP fusion protein, either Tor1-3xGFP(D330) or Kog1-3xGFP. (B) Quantification of cells with fluorescence (Vph1-CFP and/or GFP) in daughter cells, where the mother has both GFP and FM4-64 signals. Averages from two independent experiments, with n = 69 and n = 104 for GFP-Sch9, n = 166 and n = 110 for Tor1-3xGFP(D330), and n = 106 and n = 126 cells for Kog1-3xGFP, respectively. Open circles and squares indicate results of each experiment. (C) Tor1 is immediately recruited to the newly formed vacuoles. FM4-64 labeled vac17Δ cells that express Vph1-CFP from its endogenous locus, and Tor1-3xGFP expressed from a CEN plasmid with its endogenous promoter were used. Most small budded cells do not have fluorescent signals for any of the proteins, indicating that these small buds do not have a vacuole. In most cases, as the bud increases in size, Vph1-CFP and Tor1-3xGFP appear simultaneously. The middle line in the box plot indicates the median of the data set. The upper edge of the box indicates the 75th percentile of the data set, and the lower edge indicates the 25th percentile. ns; not a significant difference (p-value > 0.10); *** (p-value < 1 × 10−6). (D) Sch9 recruitment is delayed compared to Tor1, but eventually occurs. FM4-64 labeled vac17Δ cells expresses Vph1-CFP from its endogenous locus, and GFP-Sch9 expressed from a CEN plasmid with its endogenous promoter were used. In medium sized buds (0.62(±0.14) daughter size/mother size) only Vph1-CFP is present. The average bud size where both Vph1 and Sch9 are present is 0.79(±0.11). (E) Recruitment of Sch9-2D3E to the new vacuole is similar to the recruitment of wild-type Sch9. FM4-64 labeled vac17Δ cells which express Vph1-CFP from its endogenous locus, and GFP-Sch9-2D3E expressed from a CEN plasmid with its endogenous promoter were used. (F) The timing of the recruitment of Fab1 was similar to that observed for Sch9. FM4-64 labeled vac17Δ cells which express Vph1-CFP from its endogenous locus, and Fab1-3xGFP expressed from a CEN plasmid with its endogenous promoter were used. In medium sized buds (0.57(±0.13) daughter size/mother size) only Vph1-CFP is present. The average bud size where both Vph1 and Fab1 are present is 0.76(±0.10). (G) Model: The vacuole is essential for cell-cycle progression and functions in part through the TORC1 pathway. When the daughter cell receives vacuoles from the mother cell(1), the daughter can progress from G1. If the cell fails to inherit a vacuole(2), the cell generates a new vacuole(3), which is followed by maturation of the new vacuole prior to G1 progression(4). Without a functional vacuole, the daughter cell arrests at G1 phase(5).