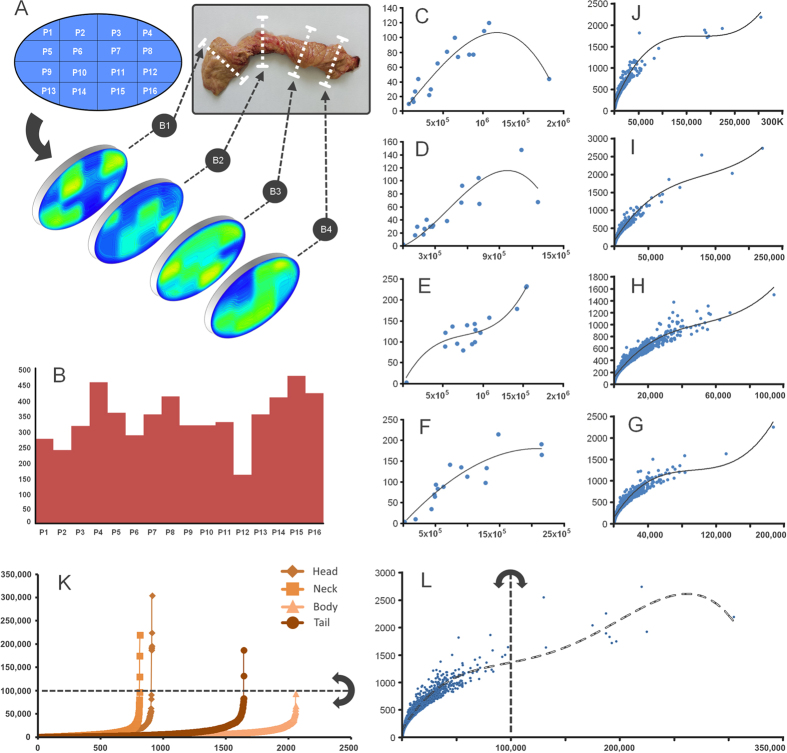
Figure 1. Distribution of pancreatic islets.
(A) a two-dimensional distribution of pancreatic islets on each section (B1–B4) of the pancreas. The pancreas from the donor and the organizational scheme of the slices are also presented. Dorsal pancreas is represented by Bx[P1-P4] slides whereas the ventral pancreas is represented by Bx[P13–P16] slides. (B) the proportion of islets along the four sections. The pancreatic islet distribution on each histological slide depending on the islet number and their average area (μm2), it is shown for the: (C) head area (B1), (D) isthmus area (B2), (E) body area (B3), (F) tail area (B4). The mean surface area (μm2) of the islets is represented on the X-axis whereas the number of islets is represented on the Y-axis. The islet number and their average area per slice (B1–B4) it is shown for the: (J) head area (B1), (I) isthmus area (B2), (G) body area (B3), (H) tail area (B4). The trend lines in panels C to H use a polynomial of order 3. (K) distribution of islets ordered by size. For each slice (B1–4), the number of islets is represented on the X-axis whereas the surface area (μm2) of the islets is represented on the Y-axis. The diamond shaped points represent islets in the head area. The square shaped points represent islets in the neck area and the points with triangular shape represent islets in the body area. The circular shaped points represent islets in the tail area. (L) a global distribution of 5423 islets depending on their perimeter and area. The dotted trend line of panel L uses a polynomial order 4. The straight dotted line and the arrows in semicircle in panel K and L, represent a barrier over which the clusters of islets have been observed.