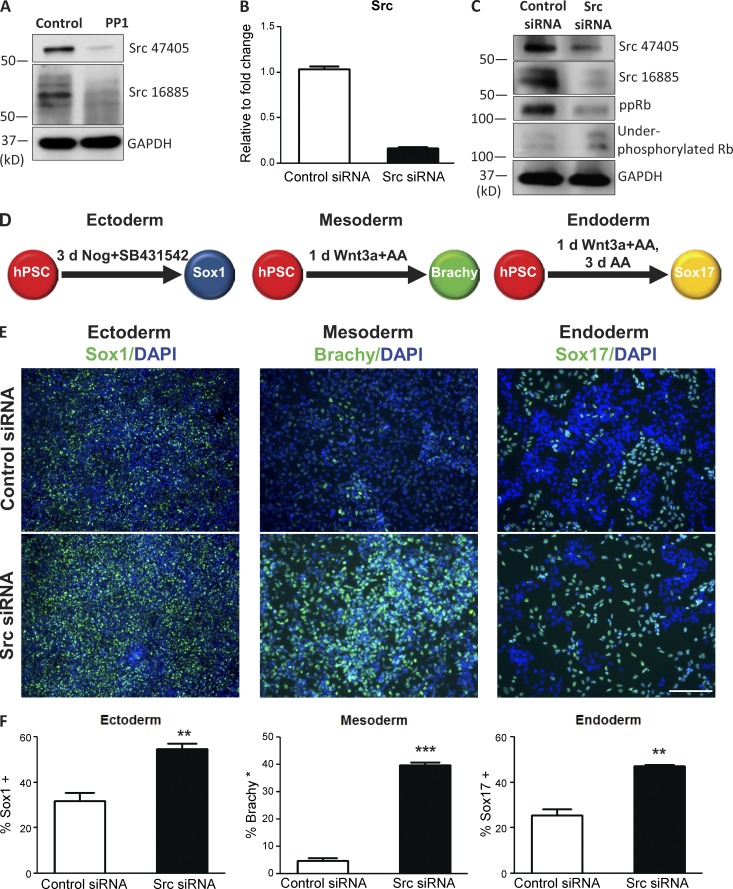
Figure 5.
Genetic suppression of Src regulates the activity of Rb and improves the differentiation capacity of hPSCs across all germ layers. (A) Western blot with Src-specific antibodies shows the levels of the Src protein after PP1 treatment of hPSCs. (B) Relative expression level of the Src gene in hPSCs transfected with Src siRNA compared with hPSCs transfected with nontargeting control siRNA. (C) Western blot with Src-specific antibodies shows the levels of the Src protein in hPSCs transfected with Src siRNA; phospho-specific antibodies show the levels of the indicated phosphorylated forms of Rb after transfection with Src siRNA. ppRb, hyperphosphorylated Rb. (D) Schematic of directed differentiation of hPSCs into Sox1+ ectodermal, Brachy+ mesodermal, or Sox17+ endodermal cells after transfection of hPSCs with control siRNA or Src siRNA. (E) Immunostaining for the indicated differentiation markers after directed differentiation in control and Src siRNA–transfected cultures. Bar, 200 µM. (F) Percentages of cells expressing the indicated differentiation markers in control and Src siRNA–transfected cultures. Error bars indicate SEM of 2–3 replicates. **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.