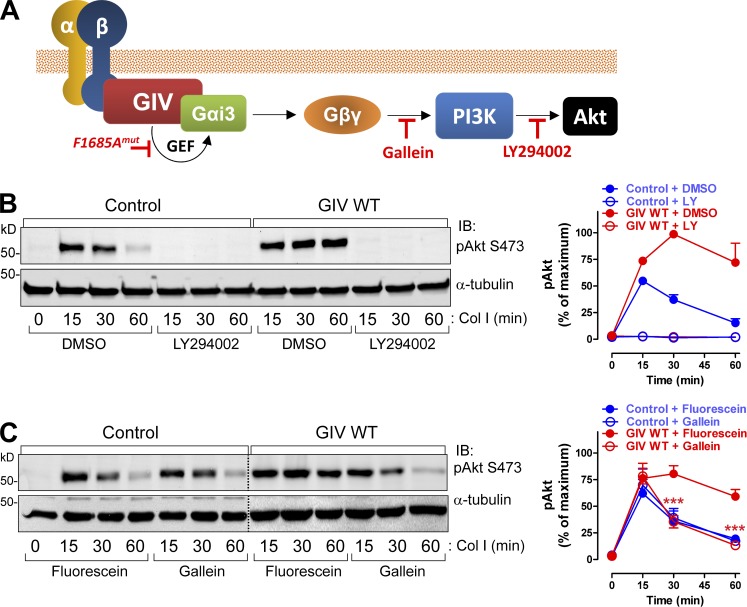
Figure 8.
GIV’s GEF activity enhances integrin-dependent signaling via a Gβγ-PI3K-Akt axis. (A) Cartoon depicting a putative GIV-Gβγ-PI3K axis linking integrin stimulation to Akt activation and inhibitors used in subsequent experiments. (B) GIV-induced enhancement of Akt signaling requires PI3K. MCF-7 cells stably expressing vector control or GIV WT were preincubated with the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 or vehicle (DMSO) for 60 min and stimulated with collagen I as described in Fig. 2 B. A representative result is shown on the left, and the quantification (n = 3; results are depicted as mean ± SEM [error bars]) is shown on the right. Blue, MCF-7 control; red, MCF-7 GIV WT; filled circles, DMSO; open circles, LY294002. (C) GIV-induced enhancement of Akt signaling requires signaling via free Gβγ. MCF-7 cells stably expressing vector control or GIV WT were preincubated with the Gβγ inhibitor gallein or its inactive analogue fluorescein for 60 min and stimulated with collagen I as described in Fig. 2 B. A representative result is shown on the left, and the quantification (n = 3; results are depicted as mean ± SEM [error bars]; ***, P < 0.001, gallein vs. fluorescein in GIV WT cells) is shown on the right. Blue, MCF-7 control; red, MCF-7 GIV WT; filled circles, fluorescein; open circles, gallein.