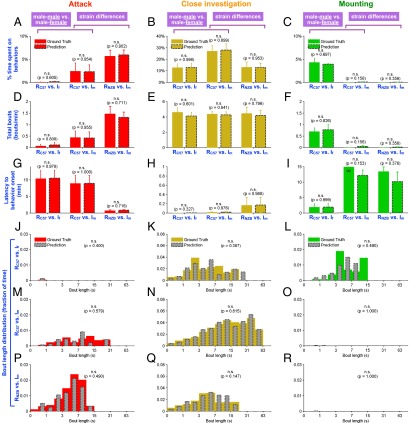
Fig. 5.
Genetic influences on social behaviors. (A–R) We examined the effects of the genetic and environmental influences on attack, mounting, and close-investigation behaviors in three different experimental conditions and validated the performance of the social behavior classifiers in these conditions. In each of panels A–I, the left two bars are from trials in which C57BL/6N male residents were tested with female intruders, the middle two bars are from C57BL/6N male residents tested with male intruders, and the right two bars are from NZB/B1NJ male residents tested with male intruders. All intruders are BALB/c. (A–C) Percentage of time spent on attack, close investigation, or mounting behavior during 15-min behavior sessions. (D–F) Total bouts per minute of individual behaviors during the same behavior sessions. (G–I) Latency to the first bout of individual behaviors during the same behavior sessions. (J–R) Histograms of behavioral bout duration (fraction of total time), as measured by the classifier and as measured by hand, for each type of resident–intruder pair and each behavior class. (J, M, and P) Attack. (K, N, and Q) Close investigation. (L, O, and R) Mounting. RC57: C57N male resident; RNZB: NZB male resident; Im: BALB/c male intruder; If: BALB/c female intruder.