Fig. 1.
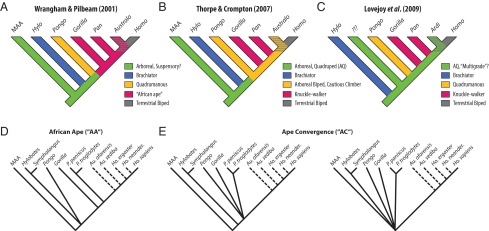
Alternative models of the hominin–panin last common ancestor (LCA). The branching pattern of living apes as inferred from genomic data is agreed upon; however, reconstruction of ancestral nodes differs among researchers. (A) In the African ape (AA) model, hominins derive from a knuckle-walking African ape-like LCA, typically conceived of as chimpanzee-like. (B and C) Ape convergence (AC) models hypothesize that the LCA is either a more generalized great ape or an unknown primitive ancestral Miocene ape. AQ, arboreal quadrupedalism. (D and E) Phylogenetic trees used to model these differences, with evolution from a common morphotype represented by a polytomy. Hominin phylogeny based on ref. 58.
