Fig. 6.
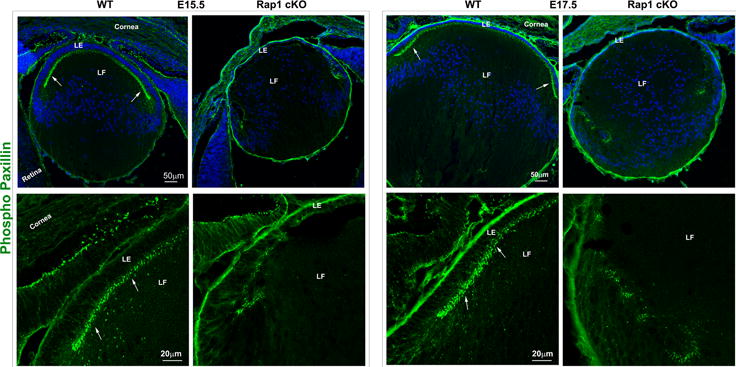
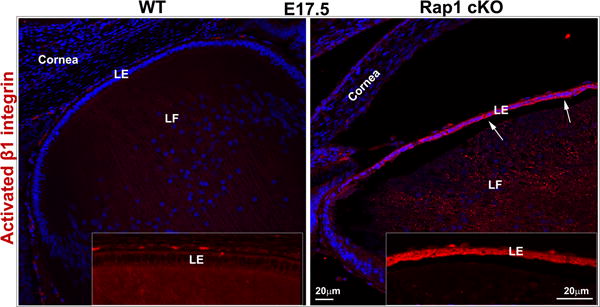
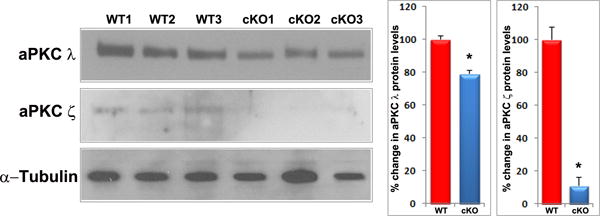
Rap1 deficiency disrupts cell-ECM adhesion, β1 integrin activation and PAR complex in mouse lens. A. To determine the influence of Rap1 deficiency on cell-ECM interactions, E15.5 and E17.5 ocular specimens derived from the Rap1 cKO embryos were evaluated for changes in activation status of paxillin based on immunofluorescence analysis of phosphorylation (Tyr118) status. In WT specimens, phospho-paxillin (green) is distributed discretely and intensely to the apical junction of epithelial and fiber cells (arrows) very similar to the distribution pattern of ZO-1. Lens capsule (both anterior and posterior) also appears to exhibit some positive staining. In Rap1 cKO (E15.5 and E17.5) mouse ocular specimens, a dramatic reduction in phospho-paxillin staining is noted at the apical junctions of epithelial and fiber cells compared with WT controls. B. Immunofluorescence analysis shows that weak staining for β1-integrin (detected using a monoclonal antibody which recognizes the activated epitope of β1-integrin) was found to be distributed throughout the WT lens, in both the epithelium and fibers (red). These specimens were also labeled for cell nuclei using Hoechst (blue). In contrast, the lens epithelium of Rap1 cKO mouse embryos showed a robust increase in β1-integrin specific staining (arrows). In lens fibers of Rap1 cKO mouse embryos, there appears to be some decrease in the staining for β1-integrin relative to WT controls. Insets depict magnified areas of the central epithelium. Bars in both A and B represent image magnification. LE: Lens epithelium, LF: Lens fibers. C. To determine the status of PAR complex activity in Rap1 cKO mouse lens specimens, the levels of aPKC (both aPKCλ and aPKCς), a well-characterized component of PAR, were examined by immunoblot analysis in E17.5 lenses and compared with respective WT lenses. The levels of both aPKCλ and aPKCς were decreased significantly in the Rap1 cKO lenses (total lysates) compared to WT controls. Immunoblots of three individual representative specimens from both WT and Rap1 cKO are shown. α-tubulin was immunoblotted as a loading control.
