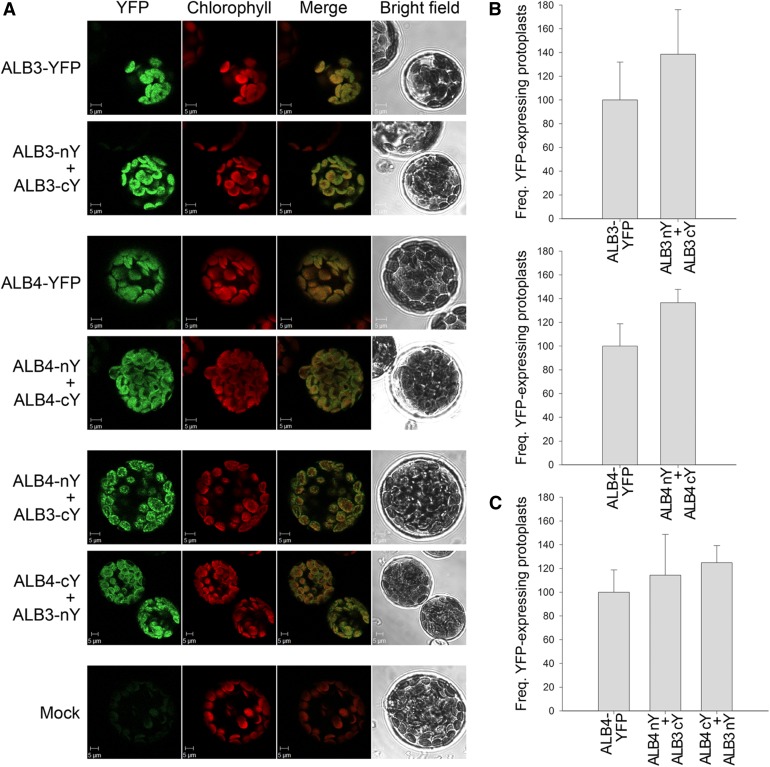
Figure 6.
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation analysis of ALB3 and ALB4 interactions. A, Wild-type protoplasts were (co)transfected with the indicated constructs and analyzed by confocal microscopy for YFP fluorescence and chlorophyll autofluorescence, and by bright-field illumination; YFP denotes fusions to full-length YFP, whereas nY and cY denote fusions to complementary N- and C-terminal fragments of YFP. The formation of ALB3 or ALB4 homodimers, and the interaction between ALB3 and ALB4 in heterodimers, is shown by the reconstitution of the YFP protein leading to fluorescence, as shown by the typical images in the respective panels. No YFP signal was detected in untransformed control protoplasts (Mock). B, The frequency (Freq.) of protoplasts that displayed YFP reconstitution via ALB3 or ALB4 homodimerization. Values for formation of the homodimers are normalized relative to the frequency observed for the respective full-length YFP construct. C, The frequency of protoplasts that displayed YFP reconstitution via ALB3-ALB4 heterodimerization (in both directions). Values for formation of heterodimers are normalized relative to the frequency observed for the full-length ALB4-YFP construct. In B and C, all error bars denote sd (n = 3).