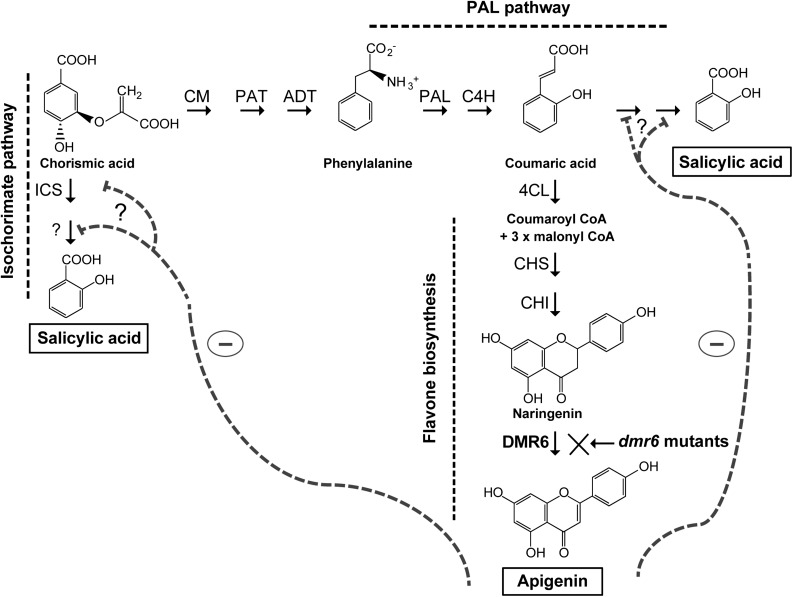
Figure 9.
Model for salicylic acid and apigenin accumulation in Arabidopsis plants. Proposed routes for the biosynthesis of salicylic acid via the isochorismatic and Phe ammonium lyase (PAL) pathways, and the flavonoid pathway to apigenin biosynthesis, are shown. In dmr6 mutant plants, a minor flow through the flavonoid pathway would lead to increased availability of substrates for salicylic acid biosynthesis. Apigenin could inhibit the activity of enzymes or the transcription of genes in the salicylic acid biosynthesis pathway (represented by gray dashed lines). Enzymes are abbreviated as follows: arogenate dehydratase (ADT), cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H), 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (4CL), chalcone synthase (CHS), chalcone isomerase (CHI), chorismate mutase (CM), and isochorismate synthase (ICS).