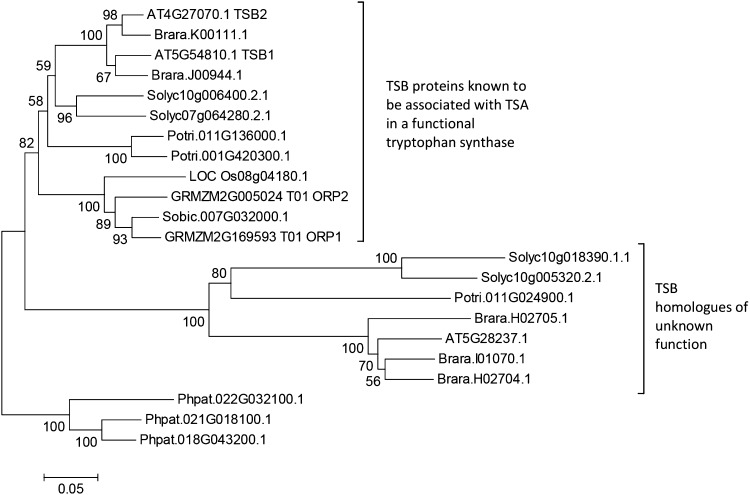
Figure 2.
Phylogeny of TSB type 1 homologs from Oryza sativa (LOC_Os), Sorghum bicolor (Sobic), Z. mays (GRMZM), Arabidopsis (AT), Brassica rapa (Brara), Solanum lycopersicum (Solyc), Populus trichocarpa (Potri), and Physcomitrella patens (Phpat). Protein sequences were downloaded from Phytozome v10.2 (Goodstein et al., 2012). The phylogenetic analysis was conducted in MEGA6 (http://megasoftware.net; Tamura et al., 2013) with multiple sequence alignment by MUSCLE (Edgar, 2004) and evolutionary history inferred using the neighbor-joining method (Saitou and Nei, 1987). The optimal tree is shown; the percentage of replicate trees in which the associated sequences clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 replicates) is shown next to the branches (Felsenstein, 1985). The tree is drawn to scale; the scale bar indicates the number of amino acid substitutions per site. It is rooted with type 1 TSBs from the moss P. patens.