Figure 6.
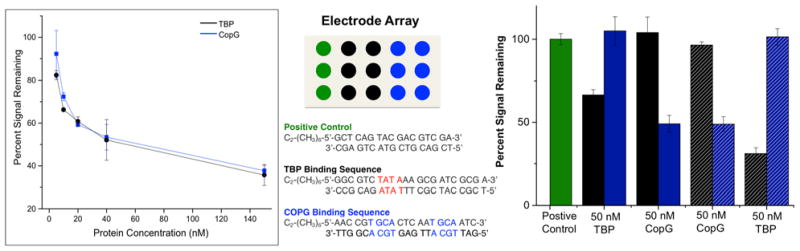
Titration of transcription factors TATA-binding protein (TBP) and CopG on two-electrode array. Each protein was titrated onto an array in concentrations ranging from 0 nM to 150 nM. Shown (left) are the percent electrochemical signal remaining from constant potential amperometry plotted as a function of protein concentration. The proteins caused significant signal decreases on the arrays in very low nanomolar concentrations. All electrochemistry was conducted in Tris buffer (10 mM Tris, 100 mM KCl, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CaCl2, pH 7.6) with 4 μM methylene blue and 300 μM K3[Fe(CN)6]. Constant potential amperometry at the secondary electrode was conducted with an applied potential of 350 mV v. AgCl/Ag to the secondary electrode and −400 mV v. AgCl/Ag to the primary electrode for 90 seconds. Specific detection of transcription factors TBP and CopG on a single array is also shown (right). Arrays are formed with six electrodes modified with DNA containing specific binding sites for each of the transcription factors TBP and CopG, as well as three electrodes containing positive control DNA that does not contain the binding site for either protein. A single protein was added to the surface at a 50 nM concentration, and the signal decrease for each sequence was monitored. The second protein was then added, and signal decreases monitored. TBP detection followed by CopG detection is shown with solid bars, while CopG detection followed by TBP detection is shown with dashed bars. The TBP binding sequence is represented by black, both in terms of the location of the electrodes modified with this sequence on the electrode array (center, black circles) and in terms of the percent signal remaining for this sequence (right, black bars). Independent of which protein was added first, signal decreases were only observed on the sequences to which the specific protein binds.
