Extended Data Figure 8. Controls for LC cTRIO.
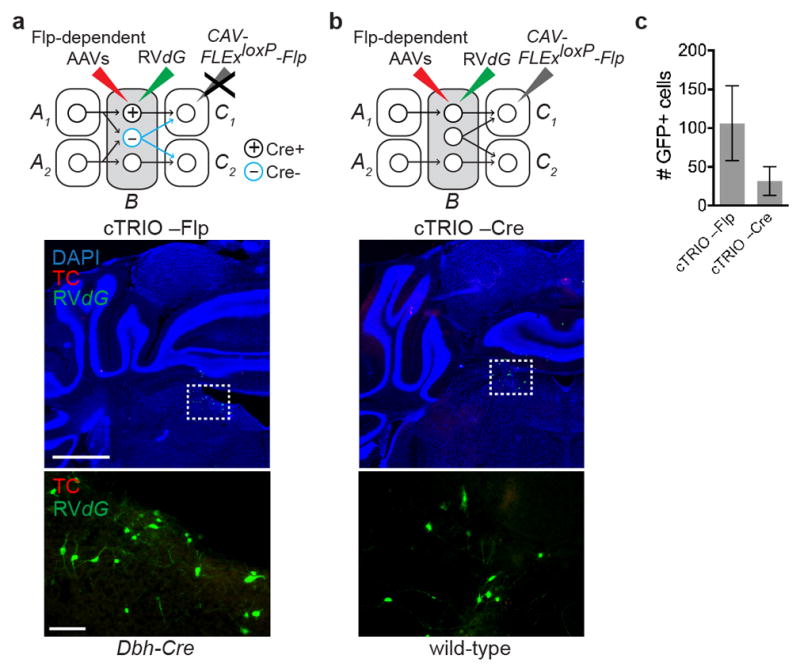
a, Top, schematic for negative controls where AAVs expressing Flp-dependent TC and G were injected into the LC of Dbh-Cre mice, followed by RVdG injection into the LC, but the CAV-FLExloxP-Flp injection was omitted. Middle, coronal section of the LC stained with DAPI (blue) shows a small number of GFP+ neurons at the injection site. The dotted rectangle highlights GFP+ neurons magnified in the lower panel. b, Top, schematic for negative control where CAV-FLExloxP-Flp was injected into the olfactory bulb and AAVs expressing Flp-dependent TC and G were injected into the LC of wild-type mice, followed by RVdG injection; hence there was no Cre to mediate Flp expression in LC cells. Middle, coronal section of the LC stained with DAPI (blue) shows a small number of GFP+ neurons at the injection site. The dotted rectangle highlights GFP+ neurons magnified in the lower panel. c, Quantification of GFP+ background labeling in the LC (n=4 and 8). This labeling is likely caused by leaky TVA expression as discussed in Extended Data Fig. 1. In none of these control experiments did we observe GFP+ or TC+ neurons > 800 μm away from the injection site. Scale, 1 mm (middle panels), 100 μm (lower panels). Error bars, s.e.m.
