Extended Data Figure 1. Controls for TRIO and cTRIO at the motor cortex (MC).
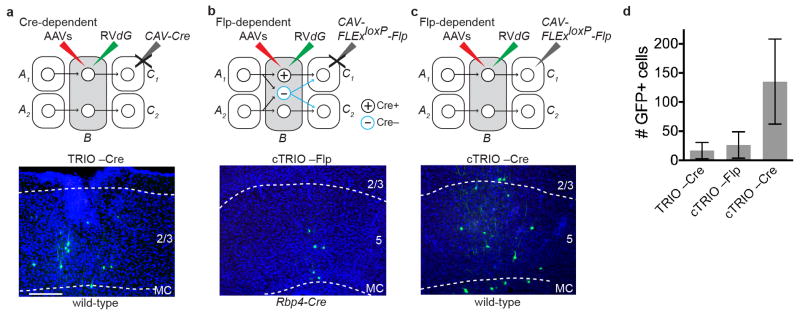
a–c, Negative control experiments omitting CAV-Cre for TRIO (a), and omitting CAV-FLExloxP-Flp (b) or the Rpb4-Cre transgene (c) for cTRIO showed only local non-specific infection of RVdG. This background labeling is likely due to Cre- or Flp-independent leaky expression of a small amount of TVA-mCherry (TC), too low for mCherry to be detected but still capable of permitting infection by EnvA-pseudotyped RVdG due to the high sensitivity of TVA10. d, Quantification for three controls (n=4, 4, 7, respectively). (By comparison, 672 GFP+ neurons were counted in the same region for an experimental brain that has the lowest starter cells among the 11 brains whose data were used for quantitative analysis of MC TRIO input tracing.) These background cells were restricted within ~500 μm of the injection site. Because of these observations, GFP+ cells on sections within ~600 μm of the injection site were excluded from the input analysis in Fig. 1g. Scale, 100 μm. Error bars, s.e.m.
