Fig. 3.
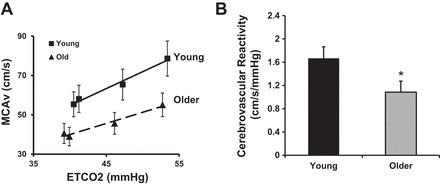
Age-associated reductions in cerebrovascular function. A: the increase in middle cerebral artery velocity (MCAv) relative to the stepped increases in end-tidal CO2 (ETCO2) is greater in young healthy adults (age: 18–35 yr) compared with older healthy adults (age: 58–76 yr). The slope of the line indicates cerebrovascular reactivity. B: cerebrovascular reactivity is significantly lower in older healthy adults compared with young healthy adults. *P < 0.05. [This image is modified from Barnes et al. (7).]
