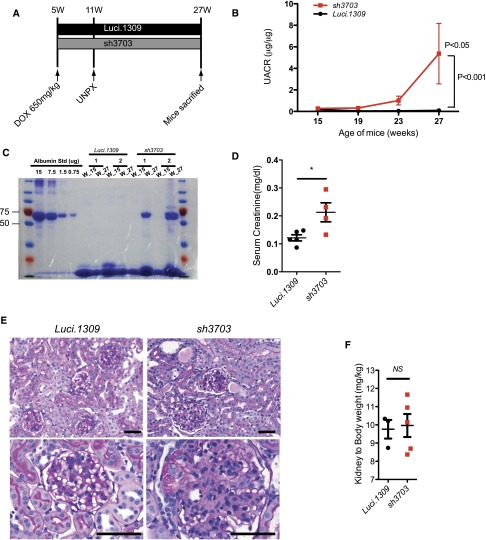
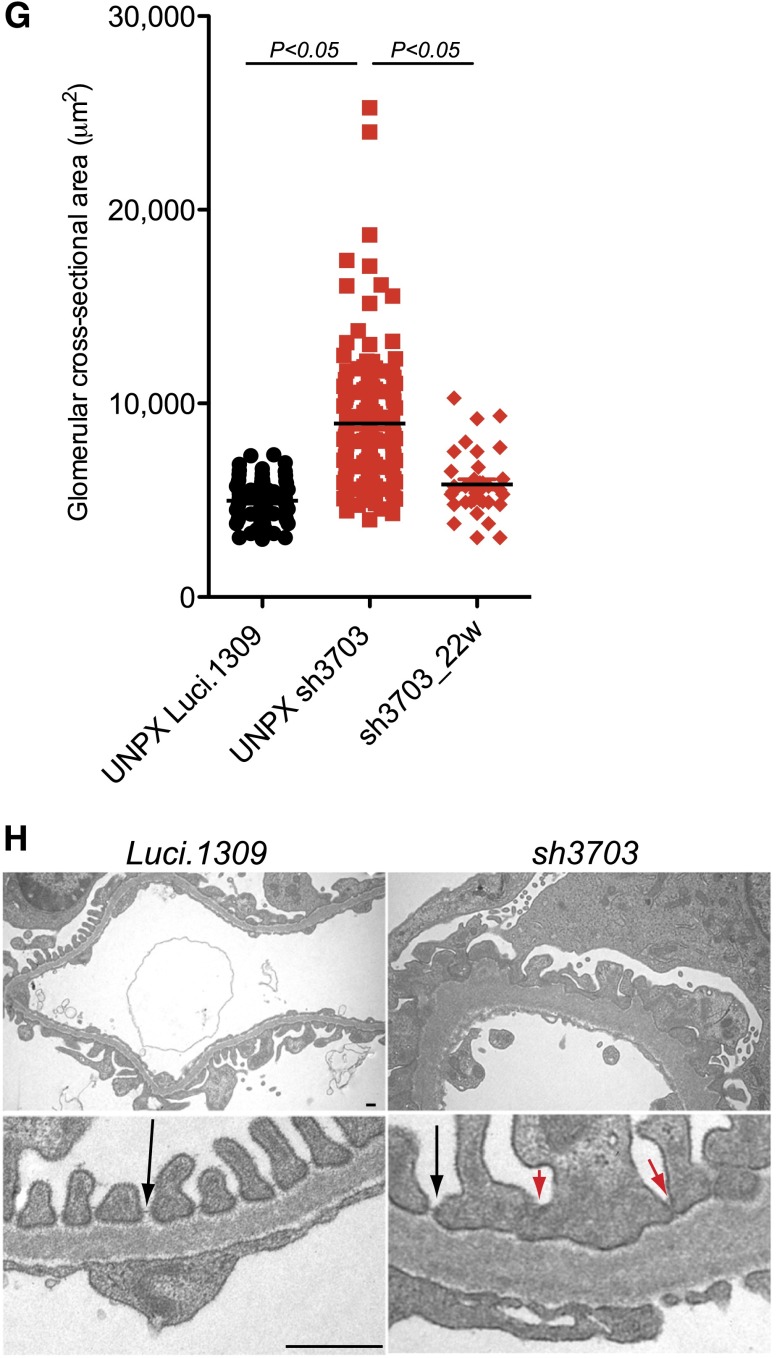
Figure 5.
Nephrin reduction promotes hyperfiltration-induced glomerular injury in uninephrectomized mice. Glomerular function and structure of nephrin knockdown mice with UNPX. (A) Schema of study design. Five-week-old sh3703 and Luci.1309 mice were induced with DOX, and UNPX was performed at 11 weeks of age. Mice were euthanized at age 27 weeks. DOX induction was continuous from ages 5 to 27 weeks. (B) Urinary albumin excretion as quantified by the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR). P<0.05 compared with the sh3703 group at 15 weeks of age. P<0.001 compared with the Luci.1309 group at 27 weeks of age. (C) Urine (7.5 μl per lane) from each of the indicated mice obtained at 15 and 27 weeks of age was analyzed on a 10% denaturing polyacrylamide gel together with 15, 7.5, 1.5, and 0.75 μg BSA and then stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R250. (D) Bar graph of serum creatinine levels of mice at 27 weeks of age as determined by an HPLC-based measurement. *P<0.05. (E) Graph of kidney-to-body weight ratios for the remnant kidney for the indicated mice at the end of the experiment. (F) Representative histologic sections of mice at age 27 weeks. (G) Graph of the cross-sectional area of the glomerular tuft for mice at age 27 weeks. **P<0.01. Scale bar, 50 μm. (H) Representative images from transmission electron microscopy for sh3703 and Luci.1309 mice 16 weeks after UNPX. Glomerular basement membrane of sh3703 mice exhibits irregular thickening. Black arrows, slit diaphragms. Red arrows, filtration slits without visible slit diaphragms. Scale bar, 1μm. Error bars, SEM.