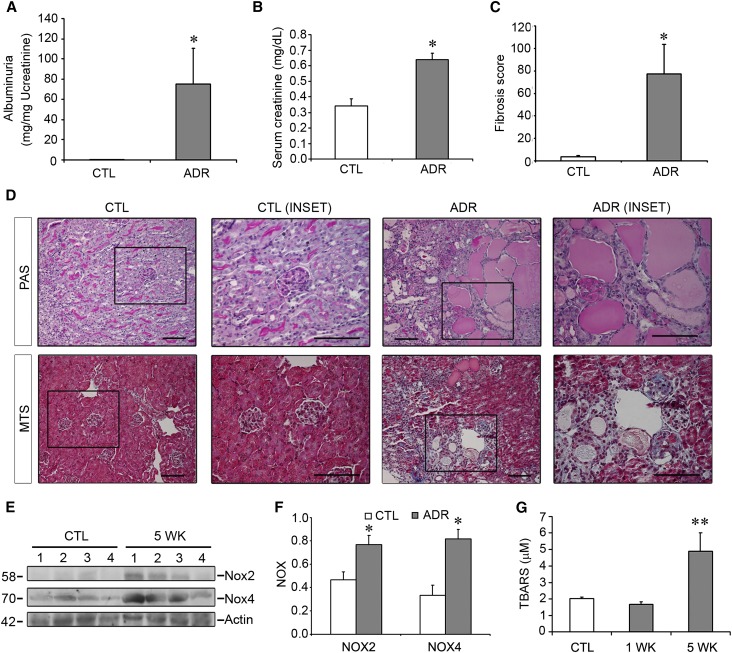
Figure 1.
Mice treated with ADR suffer from significant proteinuria and fibrosis that is associated with increased oxidative stress. BALB/c mice are treated with vehicle or ADR (10 mg/kg) and euthanized at 5 weeks after injection. (A–C) Albuminuria (A), serum creatinine (B), and renal fibrosis (C) are all increased in ADR mice compared with controls. (D) PAS stains (upper panels) reveal tubular dilation with massive proteinaceous casts in ADR mice only, whereas MTS stains (lower panels) reveal interstitial fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis. (E) The NADPH oxidase isoforms Nox2 and Nox4 are both highly upregulated after ADR. Numbers indicate individual mice. (F) Quantitative densitometric analysis of blots. (G) TBARS assay showing increased levels of this oxidative stress marker 5 weeks after ADR. *P<0.05 compared with controls at the same time point; **P<0.05 compared with both control and 1 week time points. CTL, control; PAS, Periodic acid–Schiff; MTS, Masson’s trichrome stain. Bar, 100 μm.