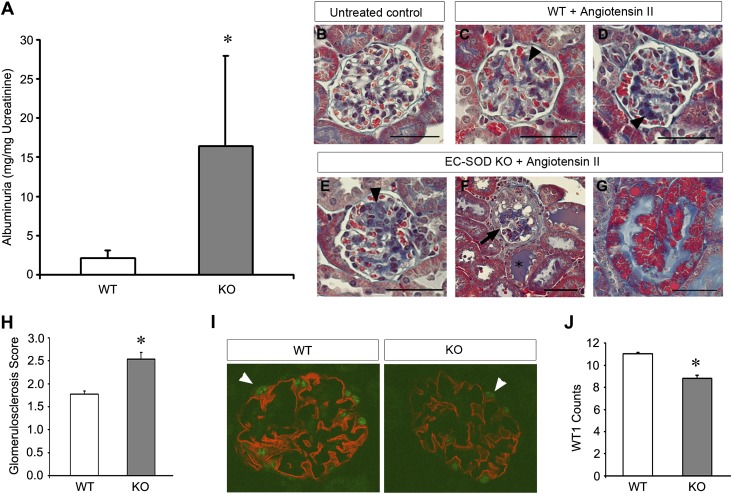
Figure 7.
EC-SOD KO mice are sensitized to angiotensin II–induced proteinuric renal injury. Mice undergo unilateral nephrectomy and are then treated with 1.5 mg/kg per day of angiotensin II via an osmotic minipump and euthanized after 4 weeks. (A–G) Albuminuria is significantly increased in KO mice compared with similarly treated WT mice. Trichrome staining shows glomerulosclerosis (arrowheads in C–E) in angiotensin II mice compared with untreated controls (B). The sclerosis lesions are further increased in the KO mice (E) and, in some cases, show heavily damaged glomeruli (arrow in F), increased cast formation (asterisk in F), and protein reabsorption droplets in some tubules (G). (H) Quantitation of the extent of glomerulosclerosis reveals greater glomerular damage in KO mice. (I) Representative micrograph of immunofluorescence double staining for WT1 (green) and nephrin (red). Arrowheads indicate WT1-positive cells. (J) Quantification of the WT1-positive cells per glomerulus are presented. *P<0.05 compared with the WT group. Bar, 50 μm.