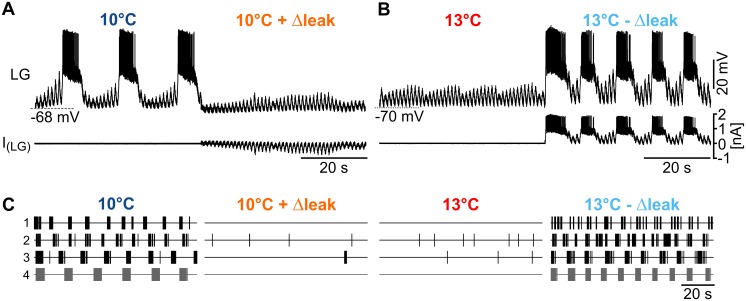
Fig 4. Changes in leak conductance are sufficient to terminate and rescue the rhythm.
(A) Top: Intracellular recording of LG during tonic MCN1 stimulation with 7 Hz at 10°C. Rhythmic activity ceased when artificial leak was added with dynamic clamp (10°C + Δleak). Bottom: Corresponding dynamic clamp current that was injected into LG. (B) Top: Intracellular recording of LG during tonic MCN1 stimulation with 7 Hz at 13°C. Rhythmic activity was recovered when artificial leak was subtracted (13°C − Δleak). Bottom: Corresponding dynamic clamp current that was injected into LG. Traces in B and C are from the same preparation. (C) Effect of artificial leak addition (10°C + Δleak) and subtraction (13°C − Δleak) on LG spike activity for all tested preparations (1 to 4). Each vertical line represents an AP in LG over 100 s of continuous MCN1 stimulation. Grey traces (4) correspond to recordings shown in A and B.