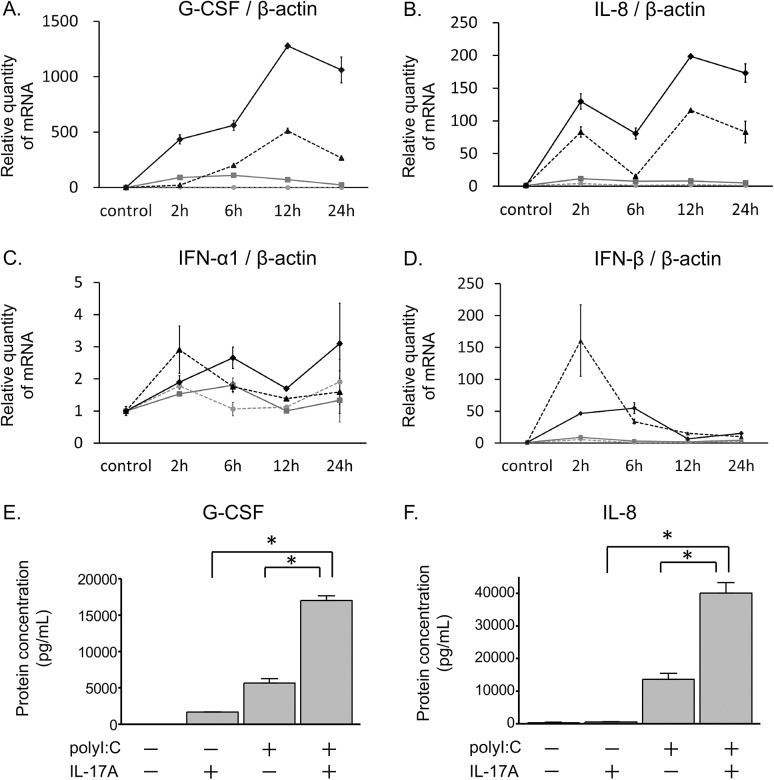
Fig 2. Time course analysis of mRNA expression and protein induction in NHBE cells.
NHBE cells in submerged cultures were stimulated with IL-17A and/or polyI:C. Total RNA was extracted from cells at different time points (0, 2, 6, 12, and 24 hours) after treatment. G-CSF (A), IL-8 (B), IFN-α1 (C), and IFN-β (D) levels were evaluated by real-time RT-qPCR and normalized to β-actin levels. Inductions of G-CSF and IL-8 mRNA expression increased over time and was significantly higher in co-treatments with IL-17A and polyI:C than in controls or other treatments. IFN-β mRNA was significantly upregulated by polyI:C or co-treatment with IL-17A and polyI:C at 2, and 6 hours. However, IFN mRNA expression was not different between polyI:C-treatment and co-treatment with IL-17A/polyI:C. Gray dashed lines with circles, unstimulated control; gray solid lines with squares, IL-17A; black dashed lines with triangles, polyI:C; black solid lines with diamonds, co-treatment with IL-17A and polyI:C. The concentration of G-CSF (E) and IL-8 (F) proteins in the conditioned medium of submerged cultures treated with IL-17A and/or polyI:C for 24 hours were detected by ELISA. Synergistic increases in G-CSF and IL-8 in protein levels were observed after co-treatment with IL-17A and polyI:C. Results are shown as the mean with S.E. of three independent experiments. * p < 0.01 versus co-treatment with IL-17A and polyI:C.