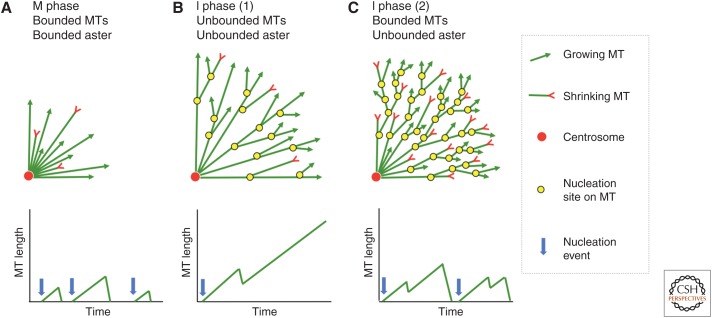
Figure 4.
Models for aster and microtubule (MT) length scaling. The top row illustrates a model for aster growth in mitosis (A) and two related models for growth in interphase (B,C). A quadrant of the aster is shown. The bottom row illustrates individual microtubule dynamics for each model, in which length fluctuations are caused by dynamic instability of plus ends. (A) Bounded mitotic aster made from bounded microtubules. Nucleation is restricted to the centrosome. Aster radius is determined by the length scale of individual microtubules. A similar model with unbounded microtubules would suffice for interphase asters in small cells. (B) Unbounded interphase aster made from unbounded microtubules. Both the aster and individual microtubules grow to cell-spanning dimensions. Nucleation away from centrosomes maintains a high density of microtubules at the periphery of the growing aster. (C) Unbounded interphase aster made from bounded microtubules. Individual microtubules are short compared with aster radius. Nucleation away from centrosomes is required at a faster rate than in B to promote aster growth.