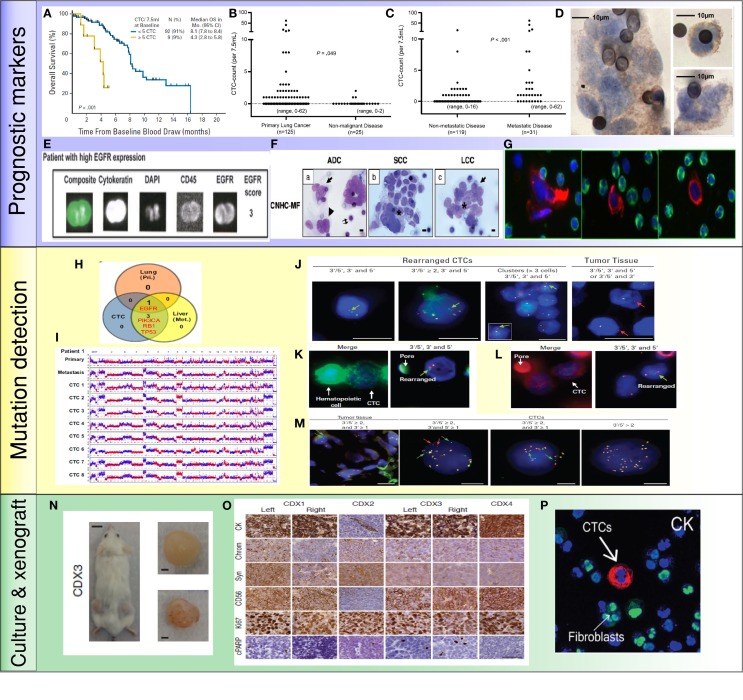
Figure 2.
Application of CTCs in lung cancer: (A) less than 5 CTCs/7.5 ml of blood predicted improved survival by CellSearch system (19). (B,C) Higher numbers of CTCs were detected in metastatic lung cancer than cancer without distant metastasis (35). (D) NSCLC CTCs were detected by ISET technology and stained positive for EGFR (36). (E) NSCLC CTCs were isolated by CellSearch system and stained positive for EGFR and CK (33). (F) Morphologic features of CTCs from different histologies of NSCLC (37). (G) CTCs were detected by HD-CTC assay and stained positive for CK (red) and negative to CD45 (green) (38). (H,I) Mutations were detected in CTCs, primary tumors, and metastatic sites. Copy number variation patterns among single CTCs, primary tumor, and metastatic sites (39). (J) ALK rearrangement patterns in CTCs and primary tumor (40). (K,L) ALK rearranged CTCs stained positive for vimentin (K) and N-Cadherin (L) (40). (M) ROS1-rearranged CTCs were compared to primary tumor (41). (N) CTCs isolated from SCLC patients generated tumor in a mouse (42). (O) CTC-derived xenografts were stained for different protein markers (42). (P) NSCLC CTCs were isolated and expanded by a microfluidic co-culture model and stained positive for CK (27).