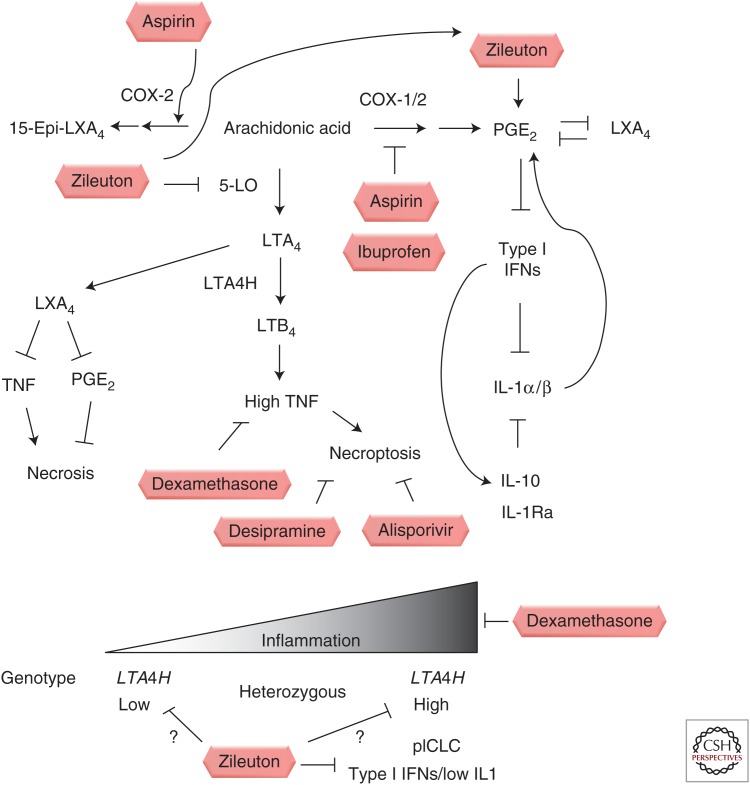
Figure 1.
Schematic of opportunities for host-directed therapies modulating eicosanoid balance. Clinically approved drugs that modulate eicosanoid production and that have been tested in animal models of mycobacterial infection are shown in boxes. Some drugs, such as aspirin, may act at multiple points in the eicosanoid pathway, whereas others, such as zileuton, may result in shunting effects. Bottom panel depicts human genotypes associated in a Vietnamese cohort with increased or decreased production of LTA4H and differential responsiveness to dexamethasone adjunctive therapy as well as a mouse model of disease in IL-1 pathway-deficient mice or animals with elevated type I interferons.