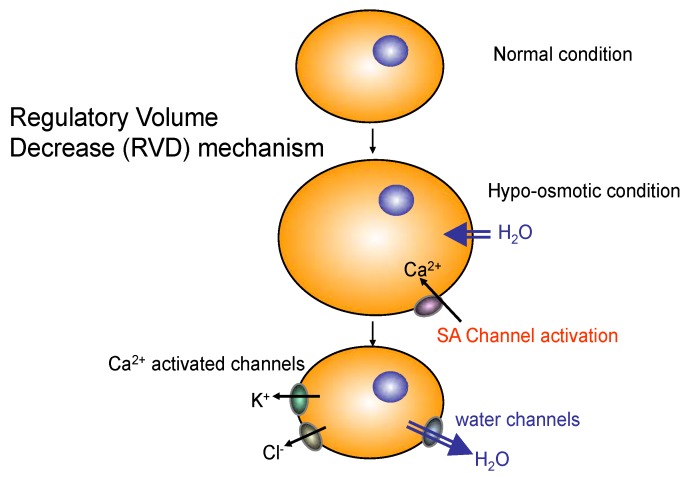
Figure 6.
The role of water channels in cell volume regulation against osmotic shock. Acute cell volume regulation is mediated by the activation of membrane ion transporters and water channels. Regulatory volume decrease (RVD) is mediated by simultaneous activation of stress activated (SA) Ca2+ channels, volume-sensitive potassium and anion channels and/or electroneutral K+, Cl− co-transporters. Volume-sensitive anion channels are permeable to Cl− and organic osmolytes (e.g., amino acids). Chronic hypo-osmolarity adaptation is accomplished by decreased expression of enzymes involved in osmolyte synthesis and a decrease in organic osmolyte content.