Figure 8.
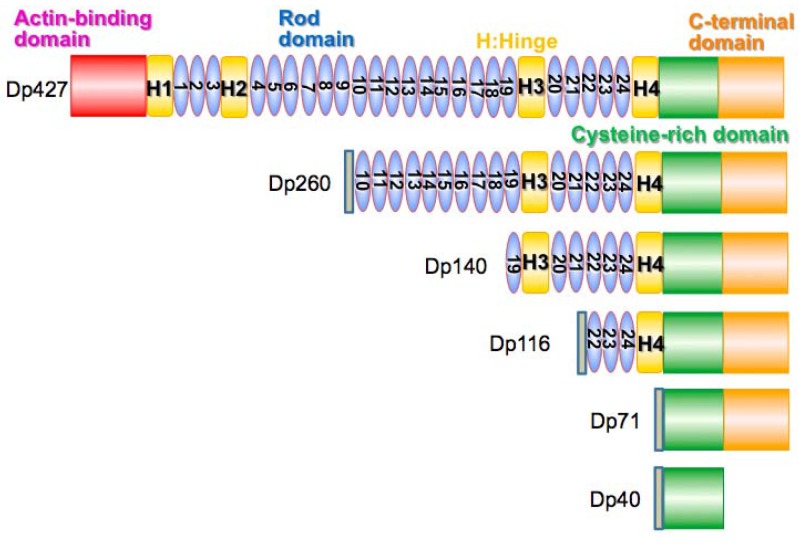
DMD/dystrophin protein (Dp) isoforms. The DMD (dystrophin) gene produces various dystrophin isoforms. The main full-length dystrophin protein is called Dp427. In skeletal muscle, DP427 has a unique N-terminal amino acid sequence, MLWWEEVEDCY, and called Dp427m (muscle) [83]. In neurons, the MLWWEEVEDCY-start sequence of Dp427m is replaced by a unique N-terminal MED amino acid sequence, and called Dp427c (cortex) [84]. In Purkinje cells in the brain, a unique N-terminal MSEVSSD amino acid sequence is expressed, and called Dp427p (Purkinje) [85]. The full-length dystrophin central rod domain contains 24 spectrin-like repeats. Dp260 is a C-terminal isoform of dystrophin expressed by an alternative promoter located in intron 29 in the DMD gene [86]. Dp260 is mainly expressed in retina, and contains 15 spectrin-like rod repeats in the rod domain. Dp140 is a C-terminal dystrophin isoform, mainly expressed during fetal brain development with an alternative promoter in intron 44. Dp140 contains six spectrin-like rod repeats, and the loss of Dp140 is associated with a higher risk of cognitive impairment in DMD and BMD [87]. Dp116 is an alternative C-terminal dystrophin short isoform, specific to Schwann cells in peripheral nerve [88]. Dp71 is a ubiquitous isoform of dystrophin expressed with an alternative promoter located in intron 62 [89]. Dp40 is the shortest known isoform of dystrophin expressed in hippocampal neuron. Dp40 is known to interact with various presynaptic proteins [90,91].