Figure 1.
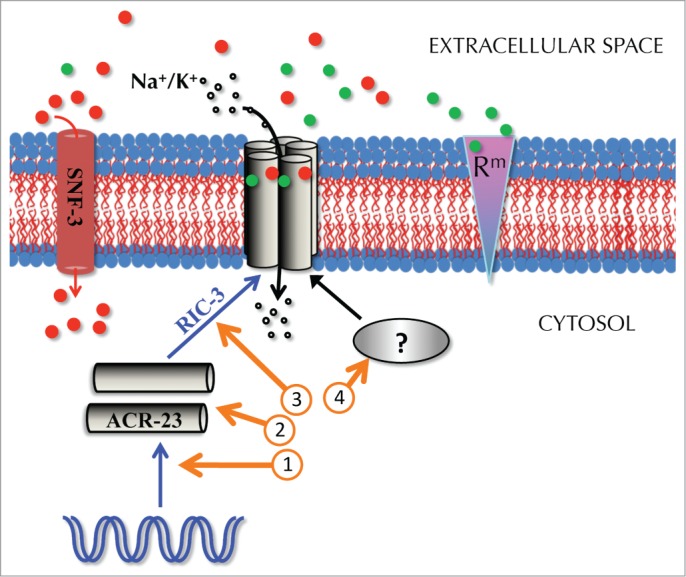
How C. elegans could develop resistance to monepantel. The ACR-23 receptor is represented by a homopentamer that transports monovalent cations (open circles) into the cytosol. ACR-23 is activated by betaine (filled red circles) and monepantel (filled green circles). Betaine is also transported across the membrane by SNF-3. The synthesis of a functional ACR-23 receptor involves several steps, which if inactivated, could result in partial or full resistance to monepantel. Such steps involve gene expression (circled “1”) and assembly of the receptor (“3”), for example by the chaperone RIC-3. In fact, ric-3 mutants are moderately resistant to monepantel.2 Mutations in the ACR-23 protein result in resistance to monepantel (“2”). Additional factors could be required for a fully functional ACR-23 receptor (“4”). Blue arrows indicate the synthesis pathway of the ACR-23 receptor. “Rm” represents a putative additional receptor to monepantel. The representation of the proteins in one single membrane tract should not imply that they are expressed in the same cell.
