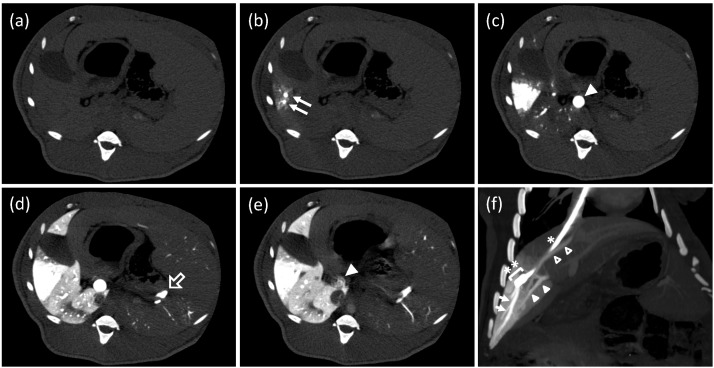
Figure 2.
Computed tomography (CT) study during a hydrodynamic injection from a catheter, which was placed at a branch of the hepatic vein. (a–e) CT images at the same axial level were repeatedly obtained with a 0.5 s interval before, during, and after a regional hydrodynamic injection of contrast medium at a constant speed of 20 mL/s in 7.5 s. Each image was taken before the injection, (a); 1 s, (b); 2.5 s, (c); 7.5 s, (d); and 12 s, (e); after the injection. Closed arrows: hepatic vein (HV) branches in the target area; closed arrowhead: main trunk of the portal vein (PV); open arrow: splenic vein. (f) An oblique multi-planar reconstruction image immediately after the end of a hydrodynamic injection before removing a balloon occlusion. The coronal image was reconstituted with a 17.7-mm thickness. A catheter (*) with a balloon (**) was placed in the branch of hepatic vein via the right jugular vein. Arrows: periphery of the target HV; closed arrowheads: portal vein of the target area; open arrowheads: another hepatic vein beginning from the inside of the target area.