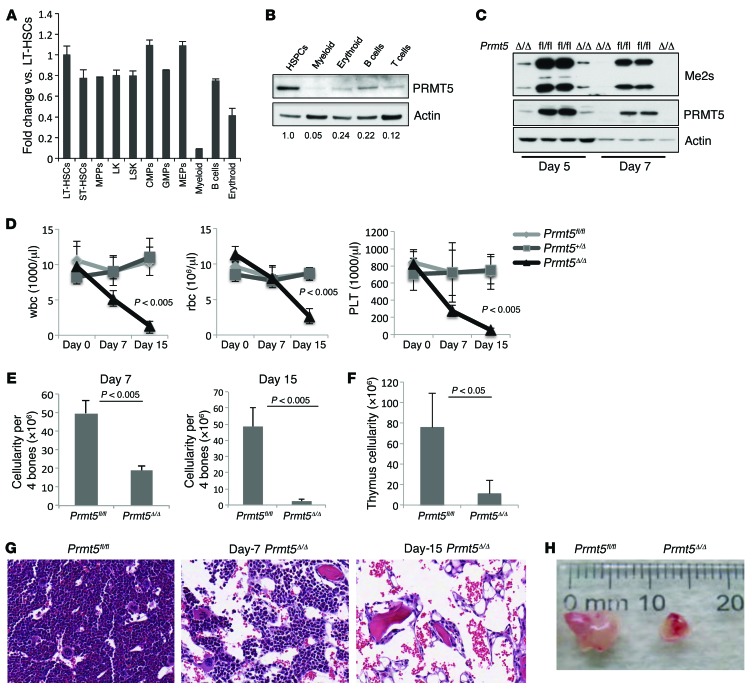
Figure 1. Deletion of PRMT5 in adult BM results in severe pancytopenia.
(A) Prmt5 mRNA levels decreased when mouse BM cells underwent terminal myeloid and erythroid differentiation. WT BM HSCs and their differentiated progeny were flow sorted on the basis of their cell surface marker expression, and Prmt5 mRNA levels were determined by qPCR (normalized to Hprt1 expression). A representative PCR result from 3 independent experiments (cells in each experiment were pulled together from 3 mice) is shown. MPPs, multipotent progenitors; CMPs, common myeloid progenitors; GMPs, granulocyte-macrophage progenitors. (B) PRMT5 protein levels were determined by Western blot analysis using sorted populations of WT BM cells. Numbers indicate the densitometry of the PRMT5 bands normalized to β-actin. (C) The cellular level of symmetrically dimethylated arginine was detected using an antibody against the Symmetric Di-Methyl Arginine Motif (catalog 13222; Cell Signaling Technology). This antibody recognizes 2 major bands of approximately 25 kDa and 15 kDa. (D) Loss of PRMT5 led to pancytopenia within 15 days. Complete blood count (CBC) analysis of peripheral blood wbc, rbc, and platelet (PLT) counts at 0, 7, and 15 days after injection (d.p.i.) are shown (n = 5). (E) BM cellularity was determined 7 and 15 d.p.i. in Prmt5fl/fl and Prmt5Δ/Δ mice (n = 5). (F) The cellularity of the thymus obtained from Prmt5fl/fl and Prmt5Δ/Δ mice was determined 15 d.p.i. (n = 5). (G) Representative images show H&E-stained cross sections of femurs isolated from the control and Prmt5Δ/Δ mice. Original magnification, ×200. (H) Representative image shows reduced size of the thymus from a Prmt5Δ/Δ mouse compared with that from a Prmt5fl/fl mouse on day 15. All P values were determined by a 2-tailed Student’s t test.