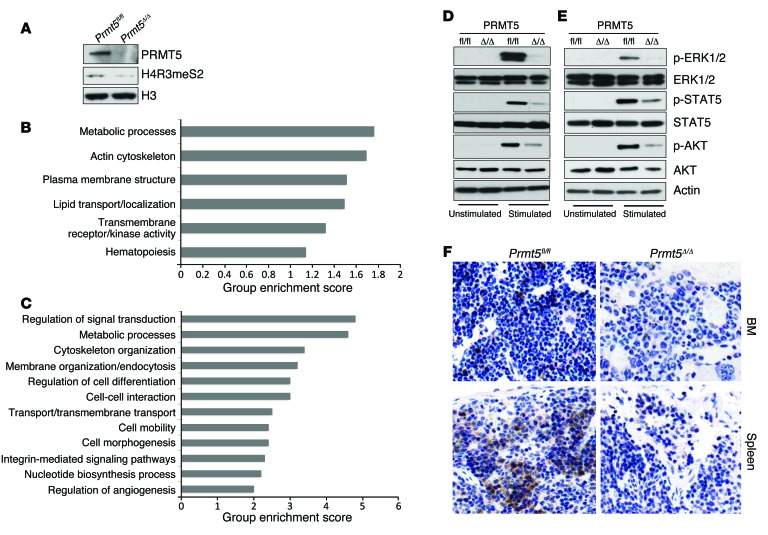
Figure 7. Impaired cytokine signaling pathways in PRMT5-deficient BM cells.
(A) HSPCs were isolated from day-3 control and Prmt5 KO mice, and the levels of PRMT5, H4R3 symmetric dimethylation, and histone H3 were determined by Western blot analysis. (B) DAVID functional pathway analysis of the differentially expressed gene set between day-3 control and Prmt5-KO HSPCs. (C) A total of 1,500 genes with intron retention in day-3 PRMT5-null HSPCs were analyzed using the DAVID functional annotation tool. (D) Total BM cells isolated from day-7 Prmt5fl/fl and Prmt5Δ/Δ mice were stimulated with GM-CSF (50 ng/ml) for 10 minutes at 37°C. Blots were probed for ERK1/2, p-ERK1/2, STAT5, p-STAT5, AKT, and p-AKT. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. (E) Purified HSPCs from control and Prmt5 homozygous KO mice were stimulated with cytokine mixture, including murine SCF (100 ng/ml), IL-3 (20 ng/ml), IL-6 (20 ng/ml), and FLT3 ligand (100 ng/ml) for 10 minutes at 37°C. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2, STAT5, and AKT was determined as in D. Three independent experiments were performed using cells pulled together from 2 mice per genotype in each experiment. (F) Paraffin-embedded femurs and spleens isolated from day-7 control and Prmt5Δ/Δ mice were immunohistochemically stained with antibodies against p-ERK1/2. Original magnification, ×200.