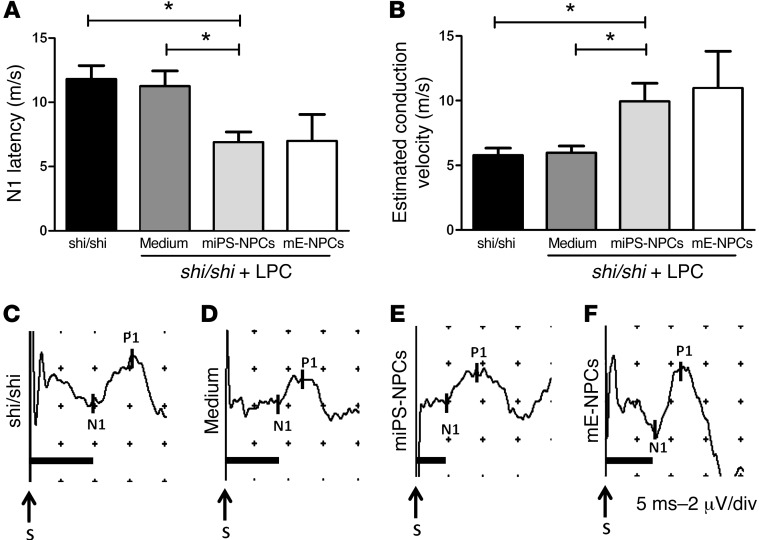
Figure 9. miPS-derived myelin improves conduction of the dysfunctional Shi/Shi Rag2–/– axons.
(A) N1 latency was measured following SSEP in different groups of Shi/Shi Rag2–/– mice 6 wpg or medium injection. miPS-derived myelin significantly decreased conduction latency in intact (P = 0.01) or demyelinated spinal cord injected with medium (P = 0.02). (B) Evaluation of axonal conduction velocity in the different groups. While no difference was detected in demyelinated and medium-treated mice over intact mice, grafted animals showed a significant increase in conduction velocities over intact (P = 0.03) or demyelinated and medium-treated mice (P = 0.02). (C–F) Representative SSEP profiles for intact (C), and lesioned mice injected with medium (D), miPS-NPCs (E), mE-NPCs (F), and grafted mice (n = 4–6 mice per group). Mann Whitney test was used for the statistical analysis. S, Stimulation. *P < 0.05. Scales in profiles: 5 ms (horizontal) or 2 μV (vertical) per divisions.