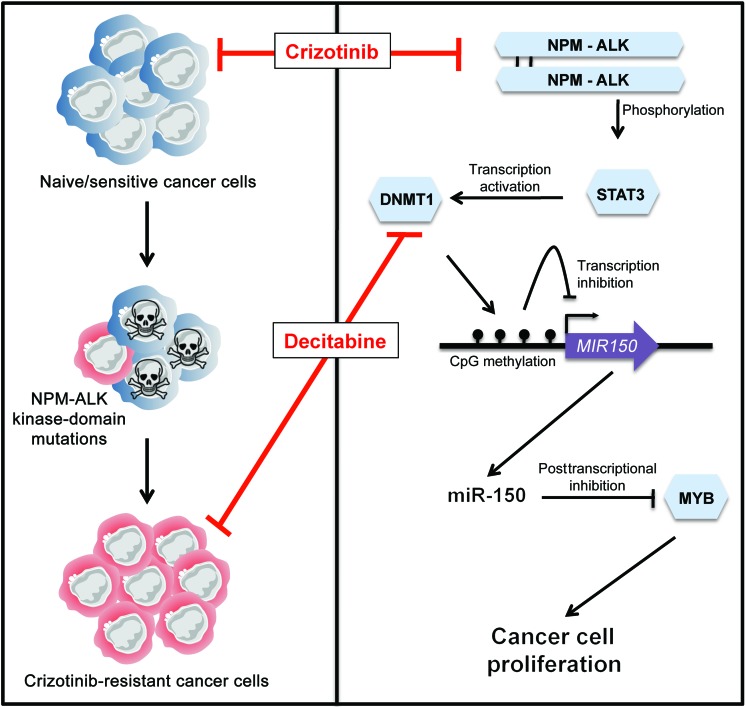
Figure 8. Schematic model of the NPM-ALK/STAT3/DNMT1/miR-150/MYB regulatory circuit in NPM-ALK(+)-associated lymphomas.
In naive/sensitive cells and cells resistant to crizotinib (an ALK TKI), the NPM-ALK fusion protein inhibits the expression of miR-150 through a DNA methylation mechanism that is dependent on the STAT3 and DNMT1 proteins. In naive/crizotinib-sensitive NPM-ALK(+) cells, crizotinib or demethylating drugs such as decitabine repress the STAT3/DNMT1 axis, thus releasing miR-150 inhibition and reducing the level of its target gene, MYB. These changes, in turn, result in decreased cell proliferation and lead to lymphoma growth inhibition. Concomitantly to its large antiproliferative effect, miR-150 expression also attenuates MYB expression in crizotinib-resistant NPM-ALK(+) cells harboring a substitution mutation within the ALK KD. These findings should promote further investigation into the effect of epigenetic modulation in other ALK-related malignancies harboring either different mutation types, different ALK fusions, or overexpressed/activated ALK full-length oncogenes. Illustration created by Servier Medical Art (http://www.servier.fr/servier-medical-art).