Fig. 1.
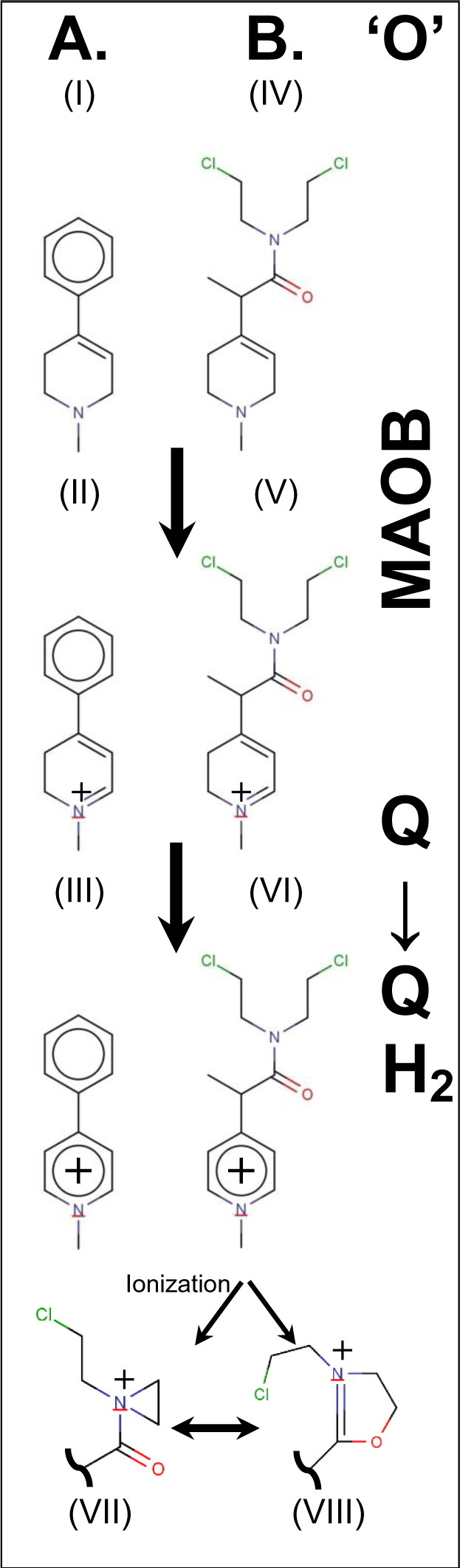
MPTP/MPMUS bioactivation pathways.
(A) Conversion of MPTP (I) to MPP+ (III) via MPDP+ (II) by sequential oxidation (‘O’); oxidation of MPTP is via MAOB and oxidation of MPDP+ is typically via the mitochondrial quinone pool.
(B) Analogous conversion by MAOB of MP-MUS (IV) to MD+-MUS (V). Again the dihydro species is converted to the pyridium, P+-MUS (VI). One of the chloroethyl groups of the mustard can ionize to give rise to either a 3-membered aziridinium (VII) or a 5-membered dihydrooxazolium (VIII) reactive ring system.
