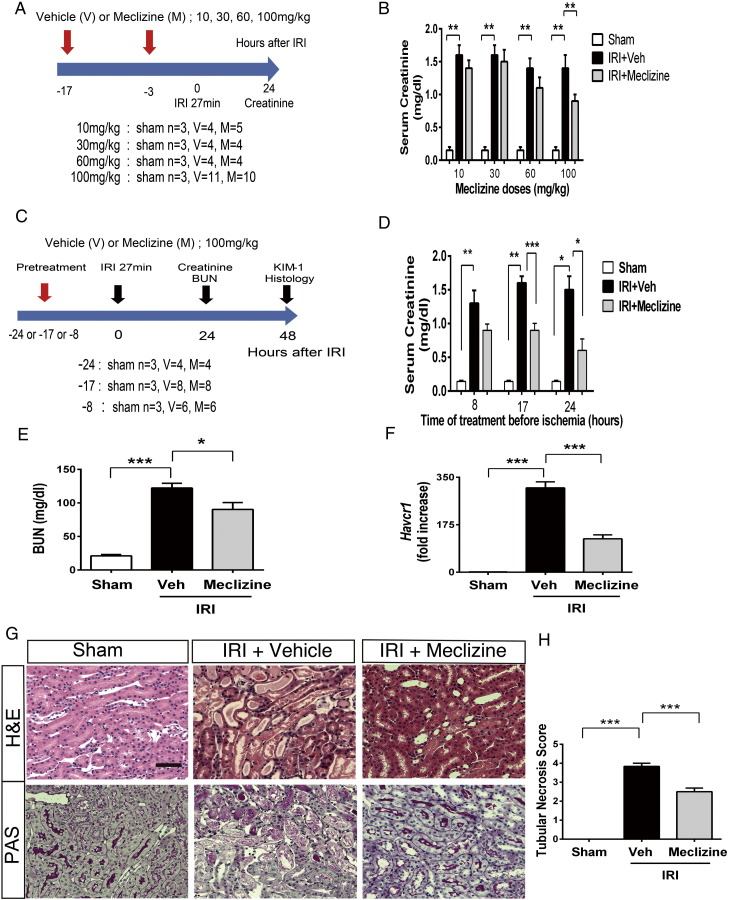
Fig. 1.
Pretreatment with meclizine protects the kidney against IRI.
(A) Scheme illustrating the strategy for the dose–response experiments. (B) Serum creatinine levels at 24 h after IRI, in animals pretreated 17 and 3 h before IRI with vehicle or various doses of meclizine. (C) Scheme illustrating the strategy comparing effectiveness of treatment at various times prior to IRI. (D) Serum creatinine levels at 24 h after IRI, in animals pretreated with a one-time injection of meclizine at different time-points before IRI. (E) BUN levels at 24 h after IRI in mice pretreated 17 h before IRI with a one-time injection of 100 mg/kg of meclizine or vehicle. Sham (n = 3), IRI + Veh (n = 8) and IRI + meclizine (n = 8). (F) Real-time PCR analysis of KIM-1 mRNA (Havcr1) in sham, vehicle and meclizine pretreated mice at 48 h after IRI. Mice were pretreated 17 h before IRI with a one-time injection of 100 mg/kg of meclizine or vehicle. Sham (n = 3), IRI + Veh (n = 4) and IRI + meclizine (n = 4). (G) Representative images after hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) and Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining of tissue taken 48 h after IRI. Original magnification 200 ×, scale bar = 100 μm. (H) Tubular necrosis was semi-quantified by scoring H&E stained slides. Sham (n = 3), IRI + Veh (n = 8) and IRI + meclizine (n = 8). ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test. The columns and error bars are the mean ± SEM.