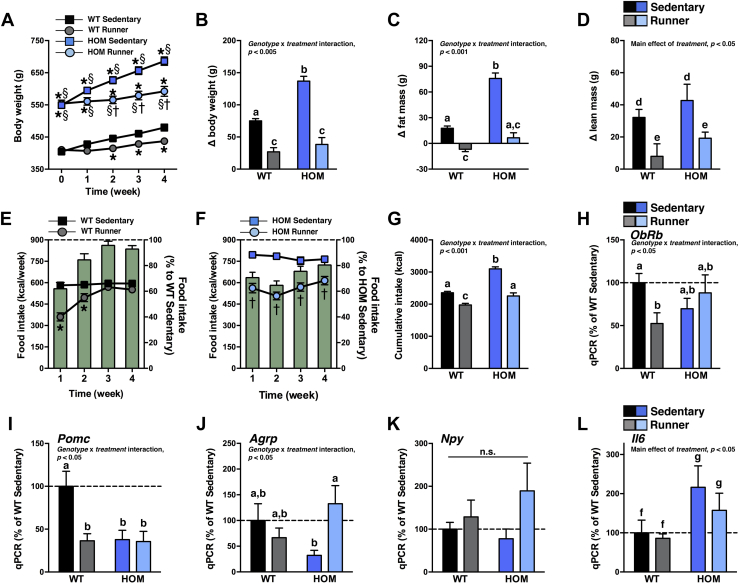
Figure 5.
Moderate voluntary exercise normalizes body weight growth and hyperphagia in HOM rats. (A) Body weight, cumulative change in (B) body weight, (C) fat mass, and (D) lean mass, and weekly (E) WT and (F) HOM food intake (kcal, left axis; % to sedentary controls, right axis), and (G) cumulative food intake of WT and HOM littermate rats without (sedentary) or with (runner) free access to running wheels for 4 wk (n = 14/group). (H) ObRb, (I) Pomc, (J) Agrp, (K) Npy, and (L) Il6 gene expression in mediobasal hypothalamus of WT and HOM littermate rats without (sedentary) or with (runner) free access to running wheels for 5 wk (n = 5–7/group). qPCR data are represented relative to WT sedentary controls. *p < 0.05, vs. WT sedentary, †p < 0.05, vs. HOM sedentary, §p < 0.05, vs. HOM wheel-runner. Different letters indicate significant difference as following: a,b,cp < 0.05, genotype × treatment interaction; d,ep < 0.05, effect of treatment; f,gp < 0.05, effect of genotype; n.s., not significant.