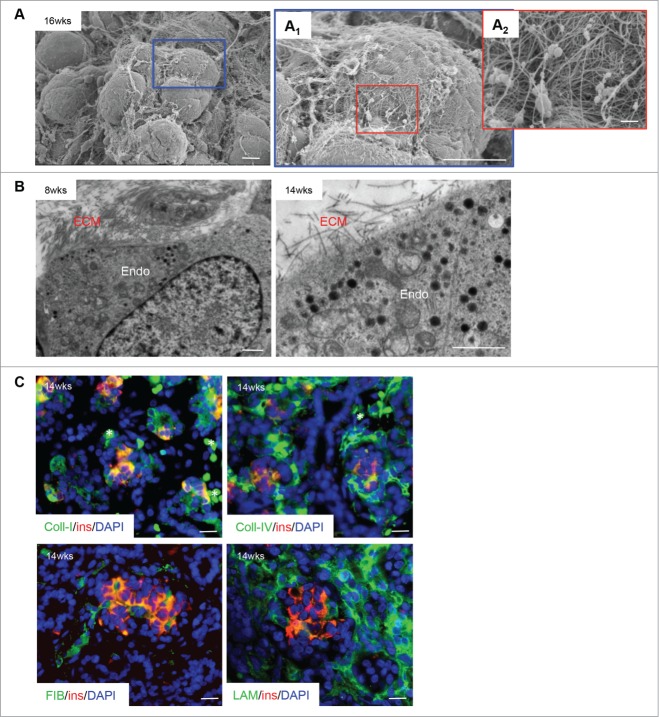
Figure 2.
Extracellular matrix localization in the developing human fetal pancreas. (A) Scanning electron micrographs of a human fetal pancreatic cluster at 16 weeks fetal age indicating a complex organization of extracellular matrix (ECM) on the cell surface. Highlighted areas are enlarged in (A1) and (A2). Scale bars = 10 μm (A and A1) and 1 μm (A2). (B) Transmission electron micrograph of ECM-endocrine cell interactions in the human fetal pancreas (8 and 14 weeks fetal age). Endo = endocrine cells, scale bars = 1 μm. (C) Double immunofluorescence staining of a 14 week fetal age pancreas for insulin (red) with collagen I, collagen IV, fibronectin or laminin (all green), and DAPI-stained nuclei in blue. Scale bar = 50 μm, asterisks = blood cells. Representative images from 4–10 pancreata are shown.