Figure 2.
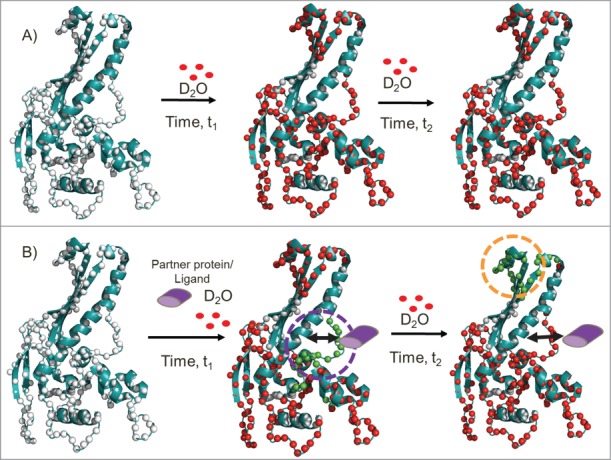
Comparative HDXMS analysis across multiple protein loci enables a distinguishing of direct protein/ligand binding from long range stabilization/allosteric sites on proteins. The schematic shows the application of HDXMS in probing protein-protein/ligand interactions. The HK-97 procapsid protein (PDB ID:3QPR) (cartoon in teal) with the backbone amide nitrogen atoms as white spheres. Deuterons (red) exchange preferentially at regions with greater solvent accessibility or that are more dynamic. Deuterium exchange of the protein at 2 different times of deuterium exchange (t2 > t1) in the absence (A) and presence of partner protein/ligand (purple) (B). In the presence of partner protein/ligand, differential decreases in deuterium exchange are observed at both proximal binding sites and distal sites. At early time points (represented by t1), reduced exchange (green) highlights the ‘direct’ binding site. With increased deuteration time (represented by t2), the binding site begins to show greater exchange arising from the reversible kinetics of association and dissociation of the partner protein/ligand, while a distal site shows reduced exchange (orange dashed lines). No differences in rates of deuterium exchange are observable between these 2 sites in the protein/ligand-free protein.
