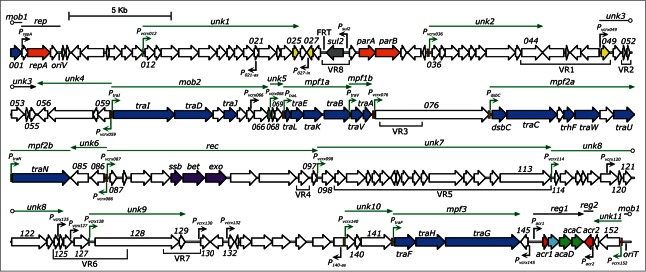
Figure 2.
pVCR94ΔX functional map. Schematic representation of the genetic organization and transcriptional units of pVCR94ΔX adapted from Carraro et al.12 The circular map of the plasmid was linearized at the start position of gene vcrx001. Genes are represented by arrows and color coded according to their function: white, unknown; blue, conjugative transfer; light blue, lytic transglycosylase; orange, replication and segregation; gray, antibiotic resistance; yellow, putative regulatory function; purple, recombination; green, activator; red, repressor. vcrx genes are indicated by their corresponding number. Variable DNA regions inserted in the conserved core of IncA/C plasmids are indicated below genes (VR1 to VR8).11 The origin of replication (oriV) and the origin of transfer (oriT) are indicated. The position of the FRT site resulting from the deletion of the antibiotic resistance gene cluster is also shown. AcaCD-binding motifs located on the positive and negative DNA strands are represented by light green and red boxes, respectively. Notable DNA clusters and operons are indicated by straight lines and arrows positioned above represented genes, respectively. Open circles mark operons and DNA clusters interruptions generated by the map format. AcaCD-regulated promoters, clusters, and operons are colored in green. mob1–2, DNA processing; rep, replication; unk1–11, unknown; mpf1–3, mating pore formation; rec, recombination; reg1–2, regulation. P021-as and P140-as: vcrx021 and vcrx140 antisens promoters, respectively. P027-in: vcrx027 internal promoter.