Figure 5. Oskar (Osk) interacts with the helicase superfamily C-terminal domain (HELICc) of Drosophila Vasa (DmVas) in vivo and in vitro.
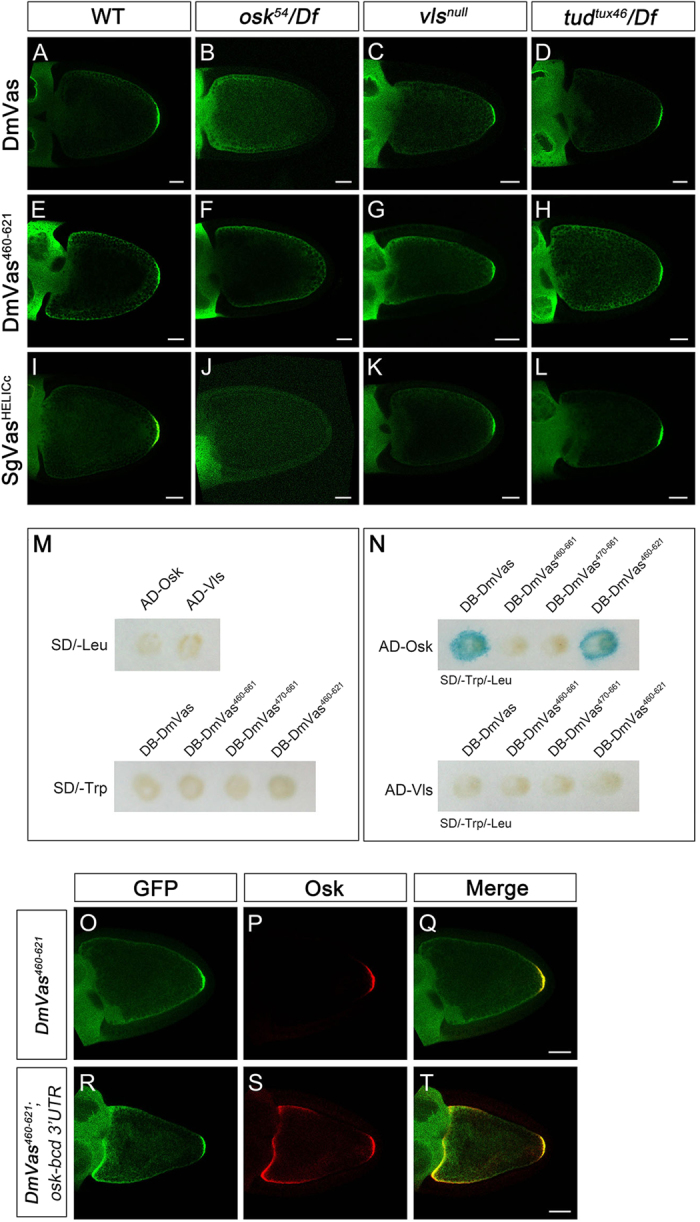
(A–L) Localisation analyses of (A–D) green fluorescent protein (GFP)-DmVas, (E–H) GFP-Vas460–621/HELICc, and (I–L) GFP-SgVasHELICc were performed in egg chambers at Stage 10 by immunostaining with the anti-GFP antibody. Genetic backgrounds: (A,E,I) Wild-type; (B,F,J) osk mutant with the genotype osk54/Df(3R)pXT103; (C,G,K) vls null mutant with the genotype Df(2L)Pr2b,P[barren+]/Df(2L)be408; (D,H,L) tud mutant with the genotype tudtux46/Df(2R)PF1. All the 3 GFP-tagged Vas proteins could be localised to the posterior germ plasm, except in the osk mutant background. (M,N) Yeast two-hybrid analysis performed using the β-galactosidase colony lift filter assay. (M) None of the singly transformed ‘bait’ and ‘prey’ plasmids could induce the expression of the lacZ reporter. (N) Osk could interact with full-length DmVas and DmVas460–621/HELICc. (O–T) Stage-10 egg chambers were stained with the anti-GFP (green) and anti-Osk antibodies (red). (Q,T) Merged images. (O–Q) GFP-DmVas460–621/HELICc was colocalised with Osk in the germ plasm. (R–T) In the egg chambers coexpressing the GFP-DmVas460–621/HELICc and osk-bcd 3′UTR transcripts, the GFP-DmVas460–621/HELICc was colocalised with Osk in the anterior and posterior poles of the oocyte. In the panels with egg chambers (A–L,O–T), anterior is to the left and posterior is to the right. The DmVas460–621/HELICc is abbreviated as DmVas460–621 in all the panels. Scale bars, 25 μm.
