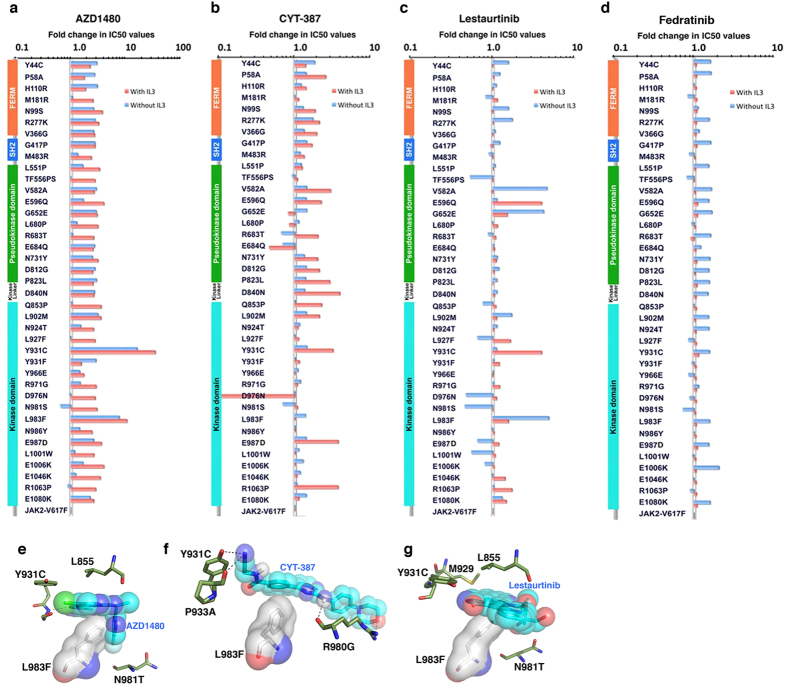
Figure 4. Ruxolitinib-resistant variants confer cross resistance to AZD1480, CYT-387 and lestaurtinib—but not to fedratinib.
IC50 values for AZD1480 (a), CYT-387 (b), lestaurtinib (c) and fedratinib (d) were normalized to 1 with JAK2-V617F and plotted on a semilogarithmic scale. Structural domains, FERM, SH2 and pseudokinase, are indicated to the left side of each graph. The most frequent and highly resistant mutation, L983F, is sensitive to CYT-387 and fedratinib. Ruxolitinib-resistant variants are fully sensitive or mildly resistant to TG10138, when cells were grown with or without IL-3, respectively. (e) Structural model of AZD1480 bound to ATP binding site, showing steric clash with phenylalanine substituted for Leu 983. (f) Structural model of CYT-387 bound to ATP binding site, showing no direct clash with bulkier phenylalanine substitution for Leu 983, explains why this variant is still sensitive to CYT-387. (g) Structural model of lestaurtinib bound to the ATP-binding site, showing steric clash with phenylalanine substituted for leucine 983.