Figure 1. ERp29 regulates post-irradiation survival of MDA-MB-231 cells.
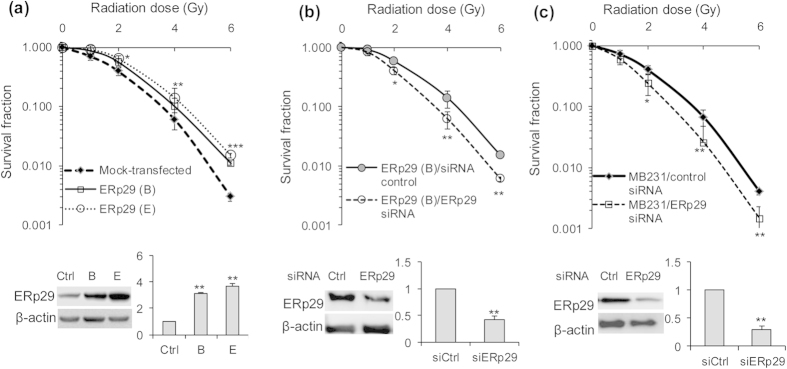
(a) ERp29 overexpression increased post-irradiation survival rate. ERp29 expressing construct was transfected into MB-231 cells and two stable clones (clone B and E) showing high expression of ERp29 were selected for radiation treatment. (b) Repression of exogenously expressed ERp29 by siRNA in the ERp29-transfected MDA-MB-231 cells (clone B) attenuated the post-irradiation survival rate. (c) ERp29 knockdown by siRNA in parent MB-231 cells reduced post-irradiation survival rate. ERp29-transfected or knockdown cells (48 hours of treatment with siRNA #1) were seeded on six-well plates and irradiated with the indicated dose of radiation. After 10 days incubation at 37 °C, colonies with >50 cells per colony were counted. The survival fraction of irradiated cells was normalized to the plating efficiency of non-irradiated control cells. The level of ER29 in ERp29-transfected cells (a) siRNA-treated, ERp29-overexpressed clone B cells (b) and siRNA-treated parental MDA-MB-231 cells (c) was examined by Western blot. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, relative to controls at the indicated dose. The level of β-actin was used as a loading control.
