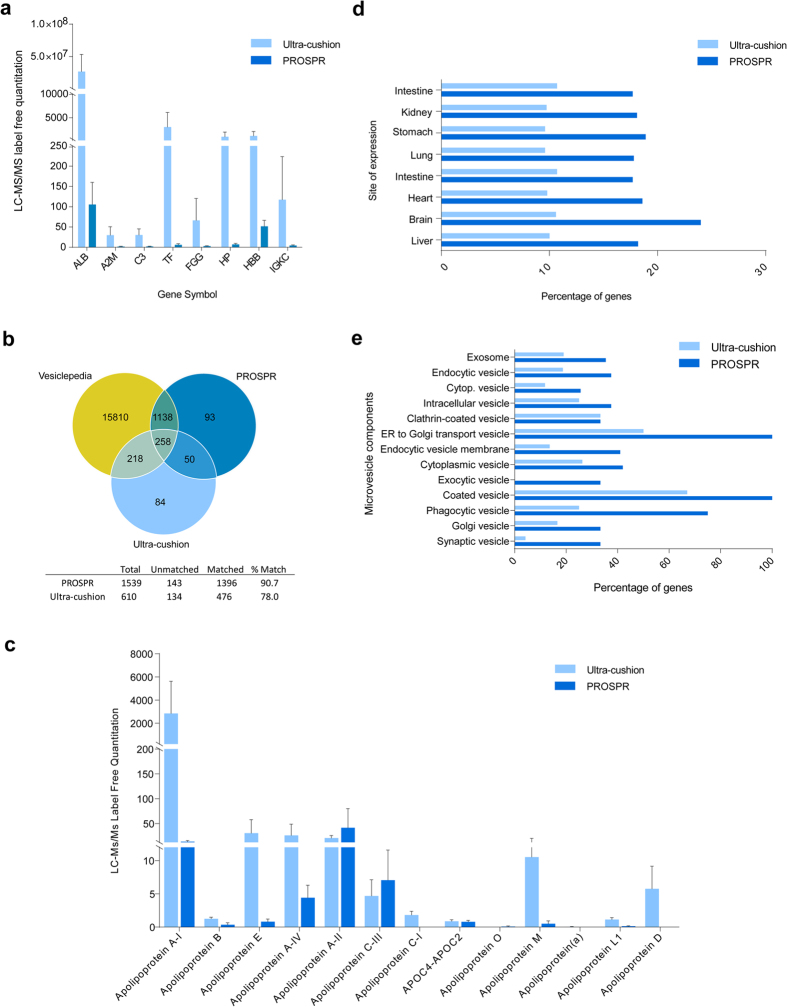
Figure 5. PROSPR generates higher purity plasma EVs as opposed to conventional ultra-cushion methods.
LC-MS/MS label-free quantitation revealed that PROSPR separation yields high purity microvesicle fractions containing lower levels of contaminating plasma proteins when compared with samples obtained by ultra-cushion (a). The list of EV proteins identified by LC-MS/MS in ultra-cushion and PROSPR isolated fractions were compared with the list of human EV proteome contained in vesiclepedia20 as shown by the venn diagrams (b). Percentage of match between ultra-cushion and PROSPR was analyzed; PROSPR revealed higher percentage of match 90.7% compared to ultra-cushion 78.0% with vesiclepedia EV proteins. Cross-contamination in ultra-cushion and PROSPR isolated EV between proteins and high density lipoproteins was analyzed (c) the lipoproteins A-II and C-III were found at higher levels in PROSPR EV fractions whereas the lipoproteins A-I, E, A-IV, M and D were found at higher levels in ultra-cushion EV fractions. EV protein datasets were subjected to functional enrichment analyses using the FunRich tool21. Higher percentage of genes was identified in PROSPR fractions compared to ultra-cushion regarding site of expression (d) and analyzed microvesicle components (e).