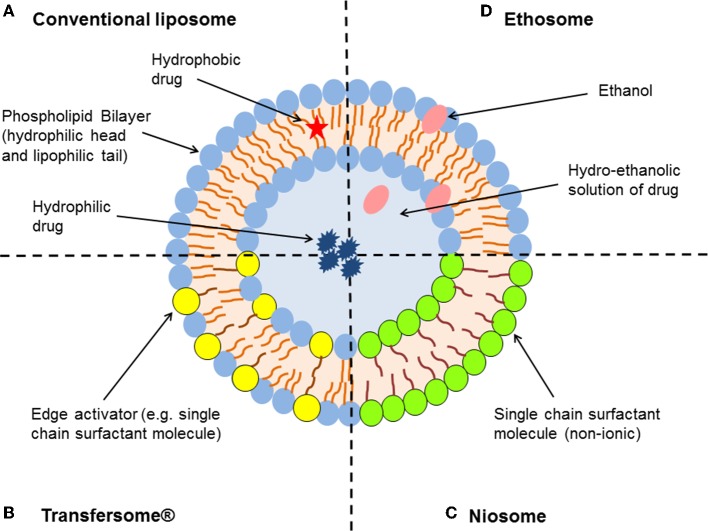
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the different types of lipid-based vesicular delivery systems. (A) Conventional liposomes generally consist of a lipid bilayer composed of phospholipids and cholesterol, which encloses an aqueous core. Both the lipid bilayer and the aqueous space can incorporate hydrophobic or hydrophilic compounds, respectively (Hua and Wu, 2013). Liposome characteristics can be modified by the addition of surfactants to form (B) Transfersomes® and (C) niosomes (depending on the ratio of phospholipid to surfactant), or relatively high concentrations of ethanol to form (D) ethosomes (Geusens et al., 2011; Vanic, 2014).