Fig. 4.
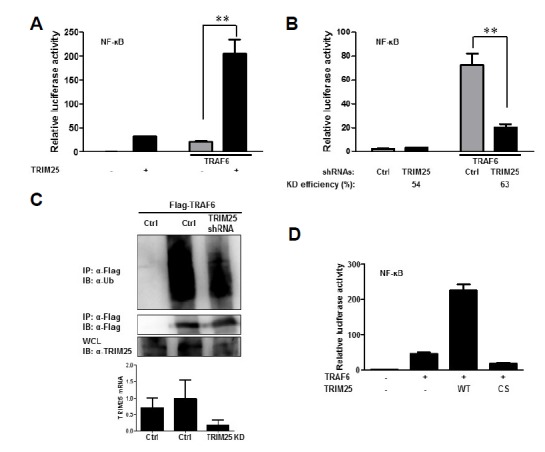
TRIM25 is involved in TRAF6-mediated NF-κB signaling. (A) Enhanced TRAF6-induced NF-κB activation by ectopic expression of TRIM25. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids as indicated. Cells were cotransfected with NF-κB luciferase reporter and TK-Renilla reporter plasmids. Promoter activities were determined by Dual-Luciferase assay 16 h after transfection. (B) Suppression of TRAF6-induced NF-κB activation by depletion of TRIM25. HEK293T cells were transfected with control shRNA (Ctrl) or shRNAs targeting TRIM25 as indicated together with reporter plasmids. Promoter activities were determined using procedures similar to those in (A). Knock-down efficiency was confirmed by measuring TRIM25 mRNA using RT-qPCR. (C) Role of TRIM25 in TRAF6 ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were transfected with flag-TRAF6 together with control shRNA (Ctrl) or shRNAs targeting TRIM25. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using an anti-flag antibody and analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies to examine the level of TRAF6 ubiquitination. Suppression of TRIM25 mRNA synthesis was confirmed by RT-qPCR. (D) E3-ligase activity of TRIM25 is required for TRAF6-induced NF-κB activation. HEK293T cells were transfected with wild-type (WT) and E3-ligase activity dead C50S/C53S mutant (CS) TRIM25 together with vector or TRAF6 plasmid. NF-κB luciferase reporter and TK-Renilla reporter plasmids were co-transfected. Promoter activities were determined by Dual-Luciferase assay 16 h after transfection.
