Fig. 1.
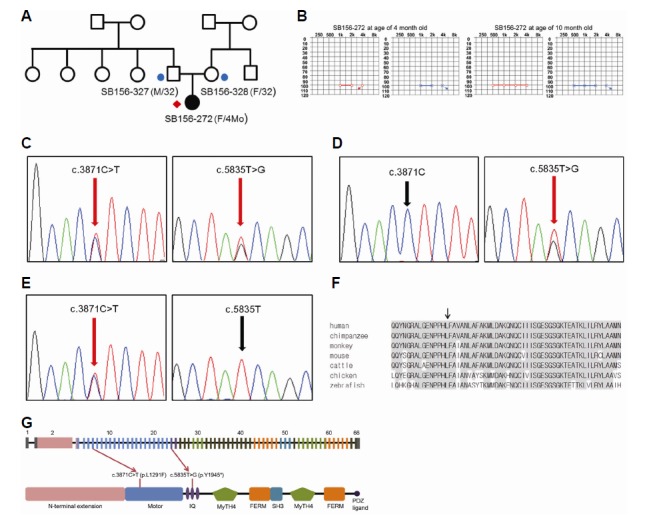
Pedigree, auditory steady state response (ASSR) and segregation of the c.3871C>T and c.5835T>G variants of MYO15A in family SB156. (A) Targeted sequencing was performed for one affected individual (red diamond). An additional two affected individuals (circles) were recruited for Sanger validation and further analyses. (B) The ASSR test revealed that the average hearing threshold of SB156-272 was 100 dB at 4 and 10 months of age. (C) Sanger sequencing traces for the c.3871C>T (p.L1291F) + c.5835T>G (p.Y1945*) compound heterozygote (SB156-272). (D) Sanger sequencing traces for the c.5835T>G carrier (SB156-327). (E) Sanger sequencing traces for the c.3871C>T carrier (SB156-328). (F) Conservation of mutant residues among orthologs from several species; p.L1291 is conserved among all species, ranging from humans to zebrafish. (G) The sequence variants c.3871C>T and c.5835T>G reside in exon 6 (motor domain) and exon 24 (IQ2 domain) of MYO15A, respectively (adapted from Nal et al., 2007).
