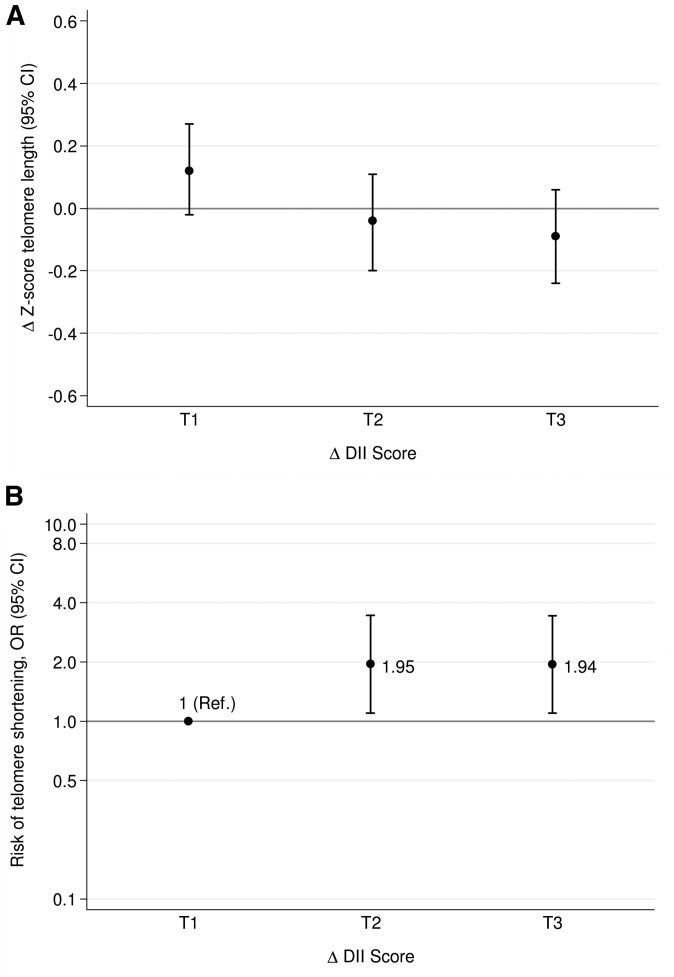
FIGURE 2.
Mean changes in telomere length z score (A) and risk of telomere shortening (B) by tertiles of changes in DII over 5 y. Adjustments were made for sex, BMI (in kg/m2), physical activity (metabolic equivalent tasks in min/d), smoking status (dichotomous), diabetes status (dichotomous), hypertensive status (dichotomous), dyslipidemia status (dichotomous), and group of intervention (3 categories). Error bars indicate 95% CIs. A change in z score ≤20th percentile indicates a high risk of telomere erosion. The y axis of panel B is log scale. Tertiles of changes in DII are −6.48 to −1.78 (T1), −1.77 to −0.58 (T2), and −0.57 to ≥3.03 (T3) after adjustment for changes in total energy intake (kcal/d) with use of the residual method. (A) ANCOVA test and linear trend test were fitted (P-ANCOVA = 0.11, P-trend = 0.04); (B) multivariable logistic regression and linear trend test were fitted (P-trend = 0.02). DII, Dietary Inflammatory Index; Ref, reference; T, tertile.