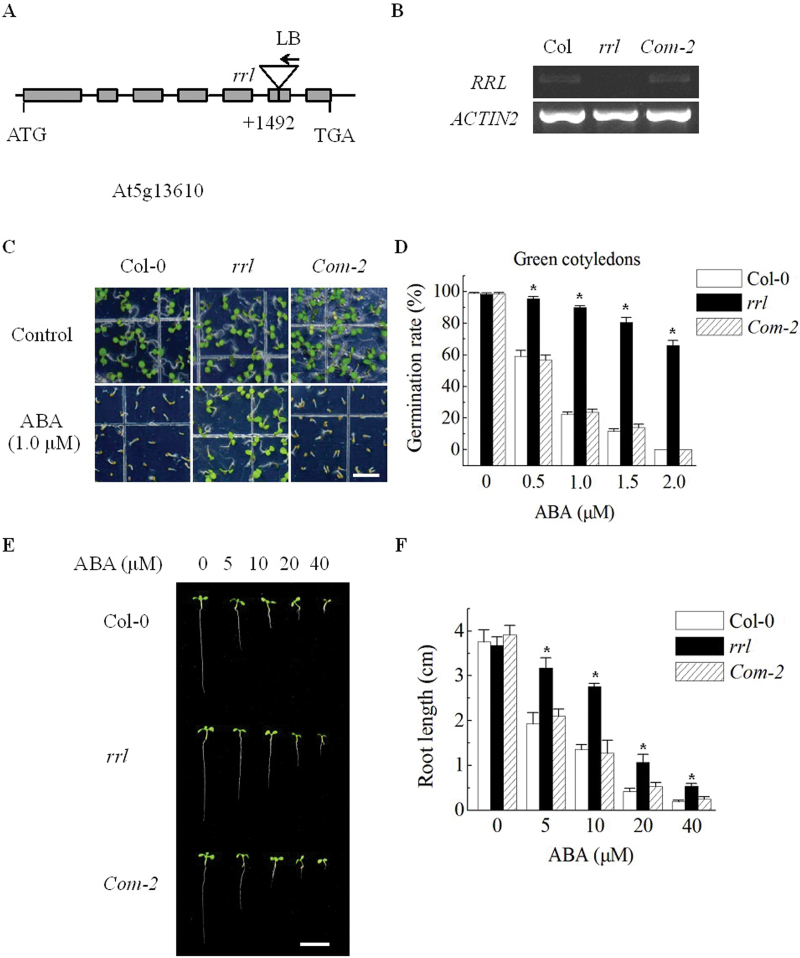
Fig. 2.
ABA-insensitive phenotype of the rrl knockout mutant in seed germination and seedling growth. (A) Schematic drawing (not to scale) of T-DNA insertion sites in the loss-of-function mutant allele of the RRL gene (At5G13610). Grey boxes and lines represent exons and introns, respectively. Arrowheads indicate orientations of T-DNA inserts. (LB, left border primer for T-DNA insertion; ATG, translation start codon; TGA, translation stop codon). (B) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of RRL gene expression in 5-day-old seedlings of Col-0 (wild type), the rrl mutant, and the Com-2 line (complementation line). ACTIN2 (AT3G18780) was used as the internal control. (C) Seeds were sown on MS medium supplemented or not with 1.0 μM ABA. Photographs were taken at day 5 after stratification. Scale bar=0.5cm. (D) Seeds were sown on MS medium supplemented with 0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, or 2.0 μM ABA. Germination rates (%) were analysed at day 5 after stratification. Values are the means ±SE of three independent experiments (n=100). *P<0.05 compared with Col-0 control. (E) Seedlings grew for 10 d after transfer from MS medium to MS medium supplemented with 0, 5, 10, 20, or 40 μM ABA. Seedlings were transferred from ABA-free medium to ABA-containing medium 48h after stratification. Scale bar=1cm. (F) Primary root lengths were assayed at day 10 after transfer. Values are the means ±SE of three independent experiments (n=50). *P<0.05 compared with Col-0 control. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)