Figure 1.
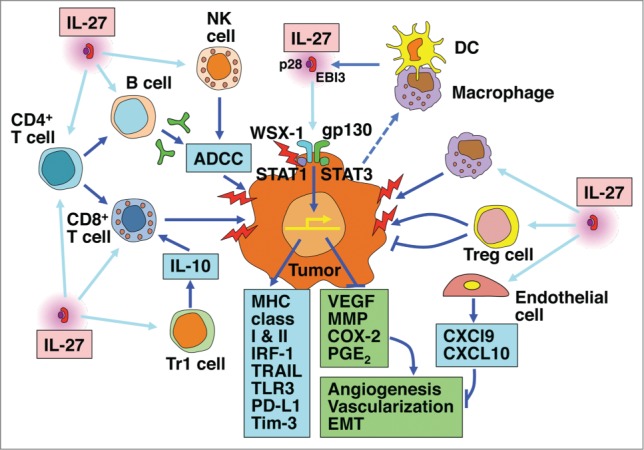
Potent antitumor activity of IL-27 through multiple mechanisms, which are mediated by CD8+ T cells, NK cells, macrophages, macrophages, ADCC, anti-angiogenesis, direct anti-proliferative effect, inhibition of COX-2 and PGE2 expression, and suppression of EMT, depending on the characteristics of individual tumors. Abbreviations: ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; DC, dendritic cell; EBI3, Epstein–Barr virus-induced gene 3; EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition; gp, glycoprotein; IL, interleukin; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NK, natural killer; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; poly(I:C), polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; Tim-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3; TLR, Toll-like receptor; Tr1, IL-10-producing regulatory T; TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; Treg, regulatory T; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
