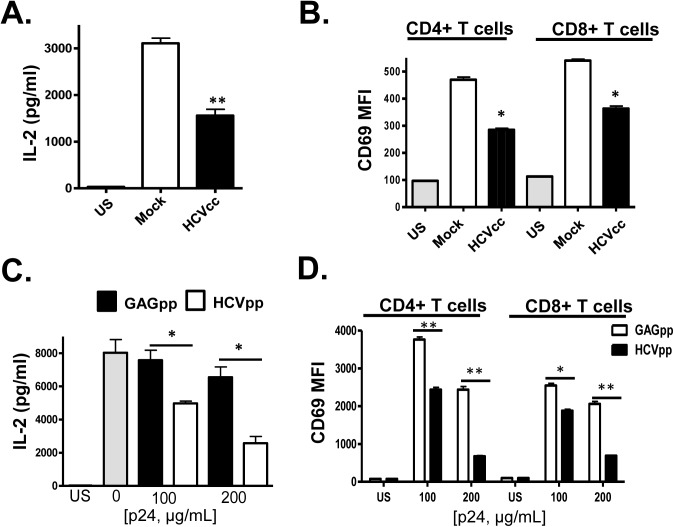
Fig 3. HCV cell culture derived particles (HCVcc) and HCV envelope pseudotyped retrovirus particles (HCVpp) inhibit T cell receptor (TCR) signaling in primary human T cells.
HCVcc produced in Huh7.5 cells inhibited TCR-mediated IL-2 release (A) and CD69 surface expression (B) in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells compared to cells incubated in mock-transfected Huh7.5 cell culture supernatant fluids following TCR stimulation with anti-CD3/CD28. Similarly, HCVpp’s inhibited TCR-mediated IL-2 release (C) and CD69 surface expression (D) compared to cells incubated in retrovirus GAG particles in a dose-related manner. US = unstimulated cells. MFI = mean fluorescent intensity. Data represent the average of three technical replicates, and the standard deviation is shown. Each experiment was independently performed with three different donors with similar results. *P< 0.05; **P< 0.01.