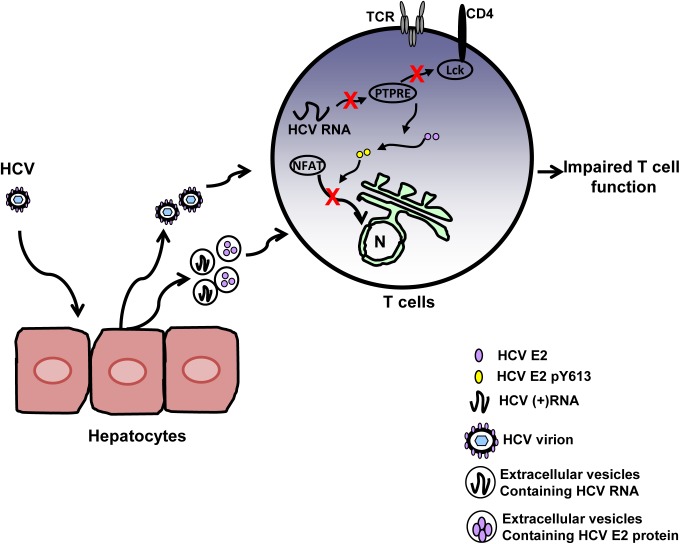
Fig 9. Proposed model for inhibition of T cell receptor (TCR) signaling during HCV infection.
HCV infection of hepatocytes results in the release of progeny HCV virions and extracellular vesicles containing HCV RNA and/or E2 protein. Viral RNA and/or E2 protein is released into T cells during particle interactions. HCV envelope RNA is processed into small RNA that inhibits protein tyrosine phosphatase E (PTPRE) expression, which results into impaired Lck activation following TCR engagement and defect in proximal TCR signaling. HCV E2 protein competes for Lck-mediated phosphorylation and phosphorylated HCV E2 at Y613 inhibits NFAT nuclear translocation, inhibiting distal TCR signaling. Inhibition of proximal and distal TCR signaling by HCV E2 RNA and protein contributes to impaired T cell function during HCV infection.